Coding Exercise 1
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
Write a Bricklayer program that uses traverseWithin and brick functions to graph the line whose slope-intercept formula is:
z = 2⁄3x + 4
Your program should graph the line in two different ways. The first line should be created using BLUE bricks and its formula should delay the integer division operation. The second line should be created using YELLOW bricks and should be calculated using conversion (from integer to real). Important: places where the lines overlap should be constructed using GREEN bricks. The result for a 16 16 baseplate is shown in Figure 1.
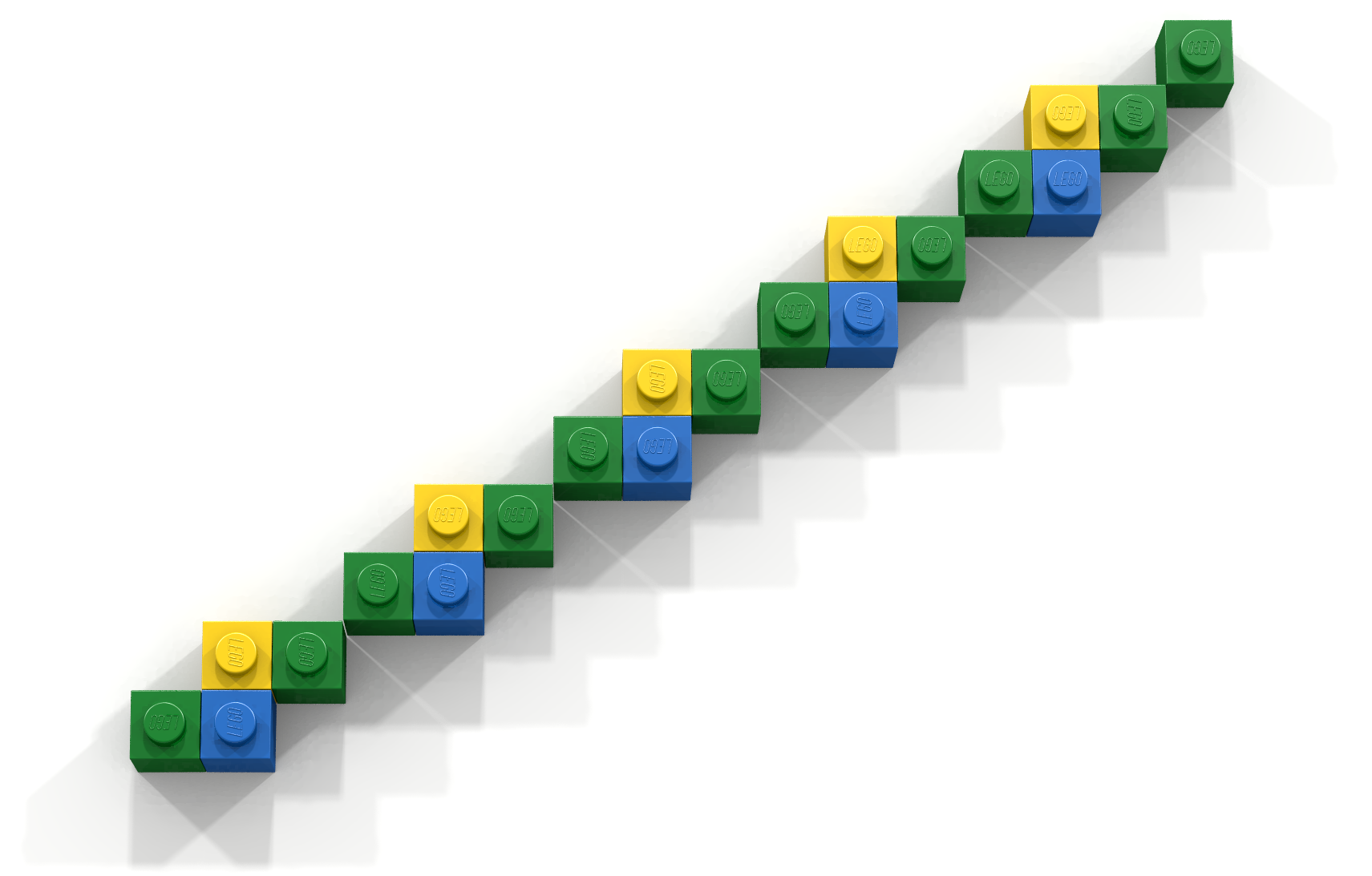
Coding Exercise 2
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
Any triangle that is not a right triangle is an oblique triangle. Write a Bricklayer program that uses traverseWithin and brick functions to create an oblique triangle whose interior is filled-in. The triangle you create must be oblique and may not contain a vertical or horizontal line as one of its sides. All other properties of the triangle are left unspecified. An example of an oblique triangle is shown in Figure 2.
Coding Exercise 3
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
A hexagon is a polygon having 6 sides. An example of a hexagon is shown in Figure 3. Write a Bricklayer program that uses traverseWithin and brick functions to create a hexagon whose interior is filled-in. The dimensions of the hexagon are left unspecied.
Coding Exercise 4
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
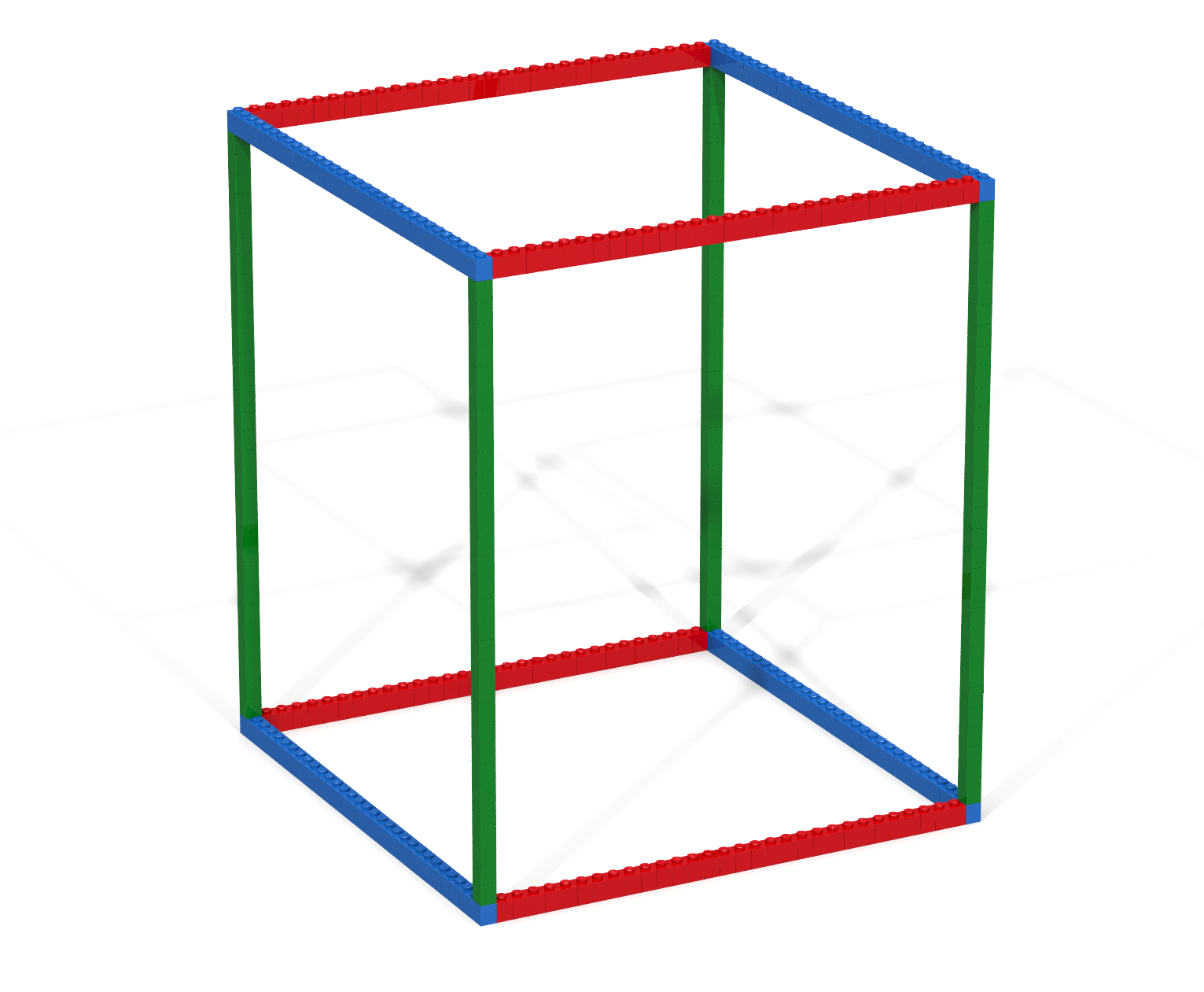
Write a Bricklayer program that uses traverseWithin and brick functions to create a wire-frame cube such as the one shown in Figure 4.
Coding Exercise 5
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
Write a Bricklayer program that uses traverseWithin and brick functions to create a cube such as the one shown in Figure 5.
Coding Exercise 6
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
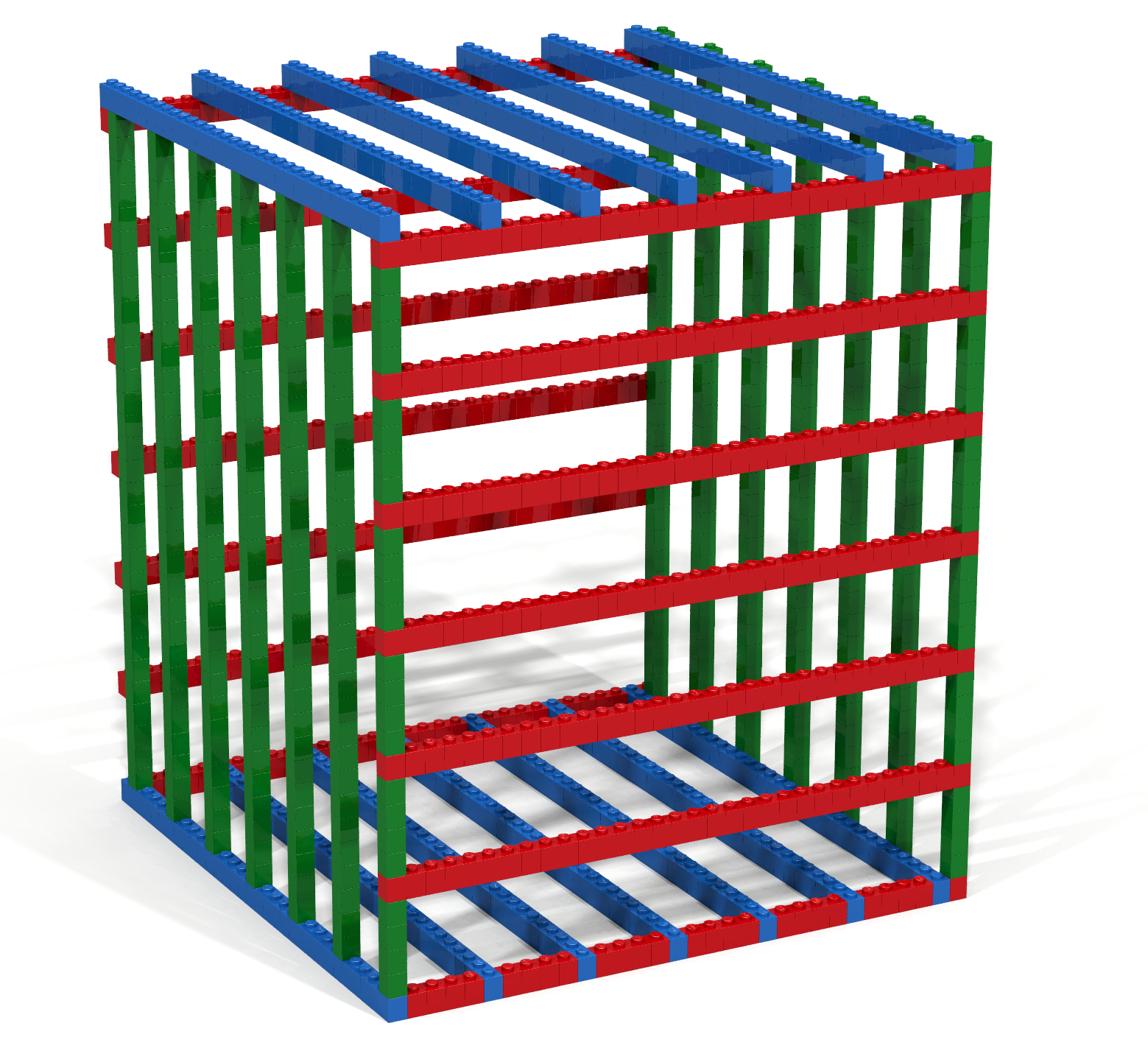
Write a Bricklayer program that uses traverseWithin and brick functions to create a cube such as the one shown in Figure 6.
Coding Exercise 7
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
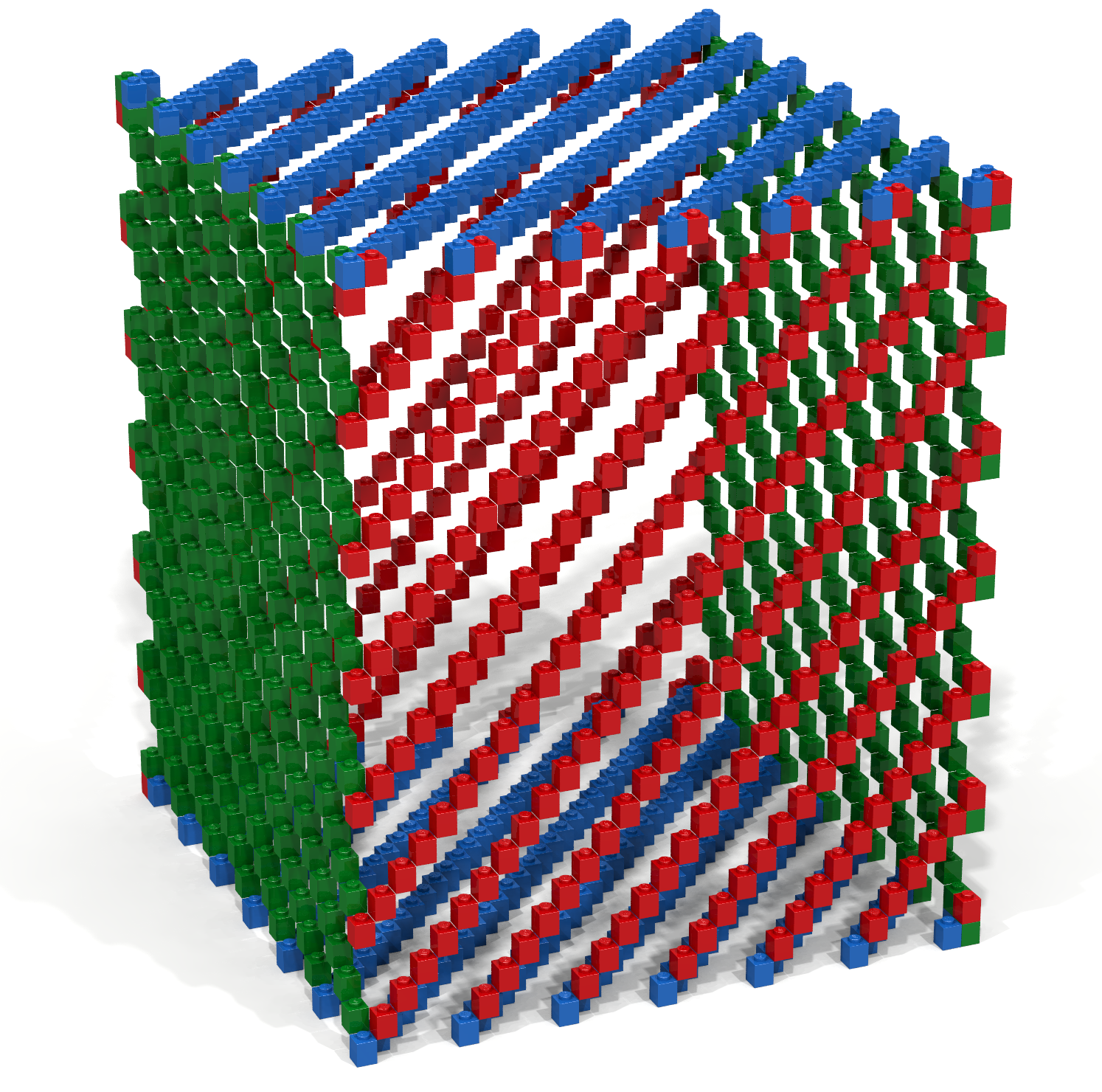
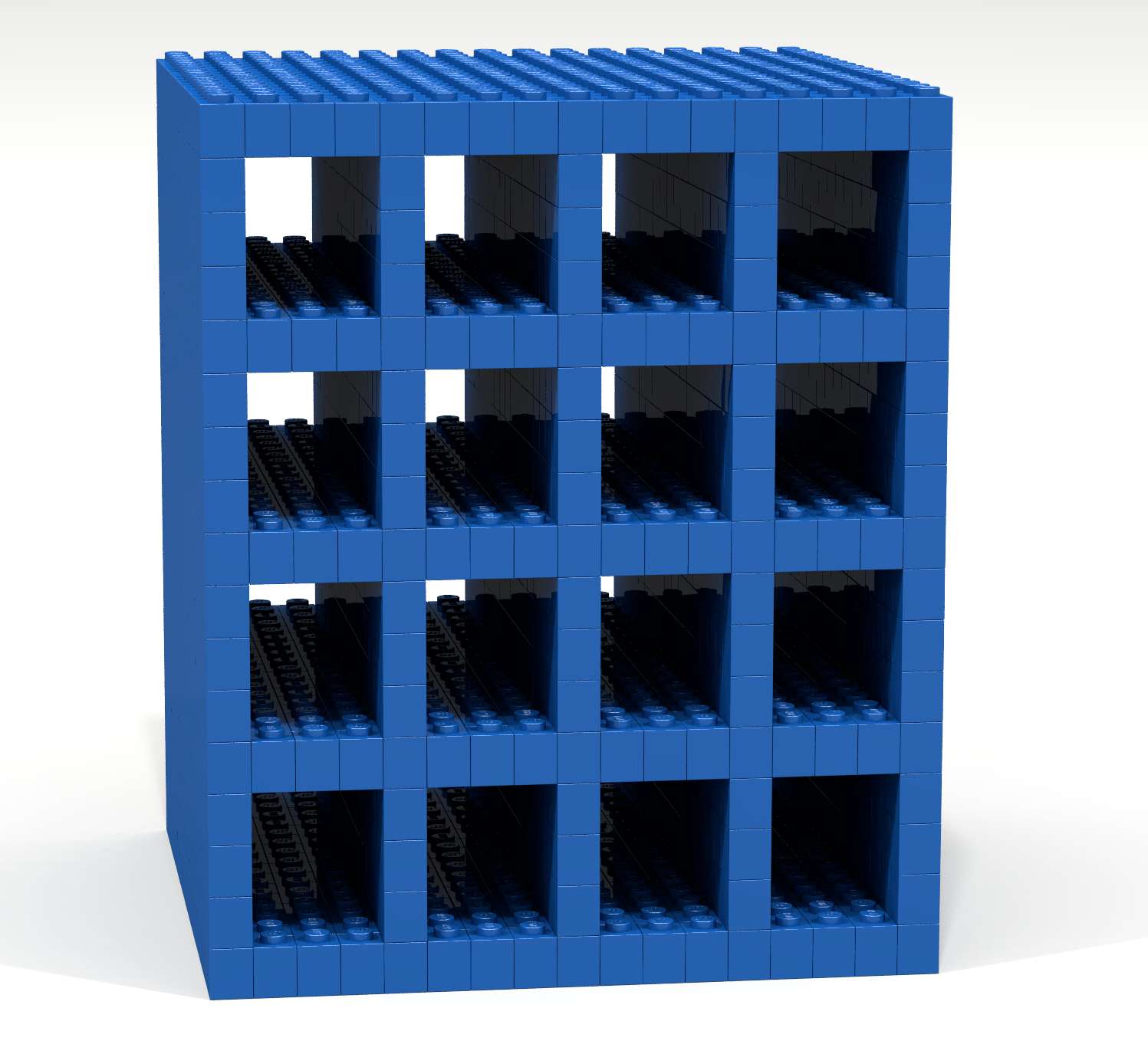
Write a Bricklayer program that uses traverseWithin and brick functions to create a storage cube such as the one shown in Figure 7.
Coding Exercise 8
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
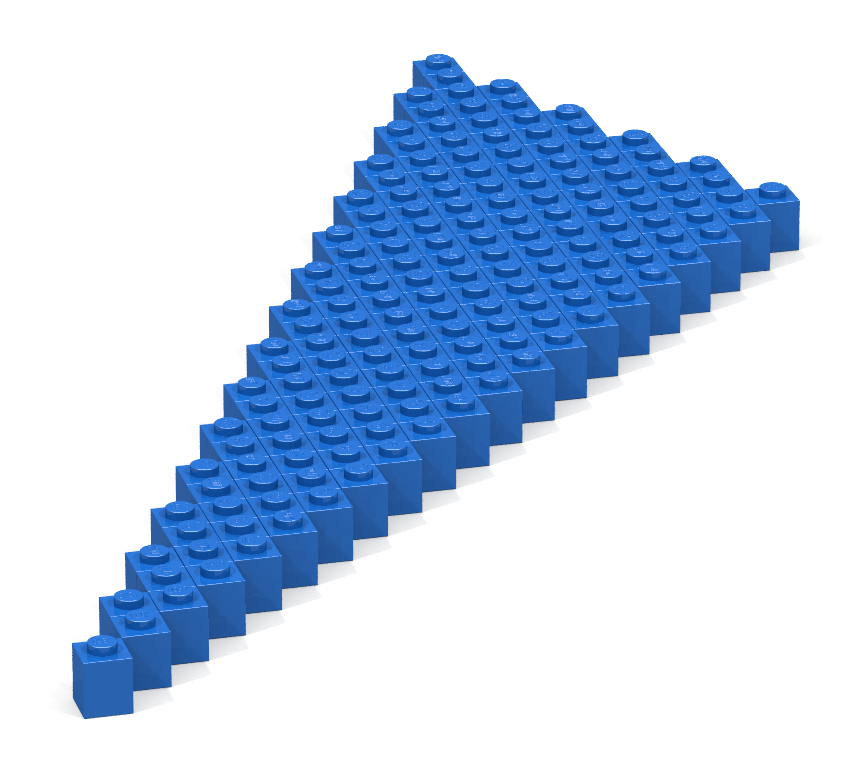
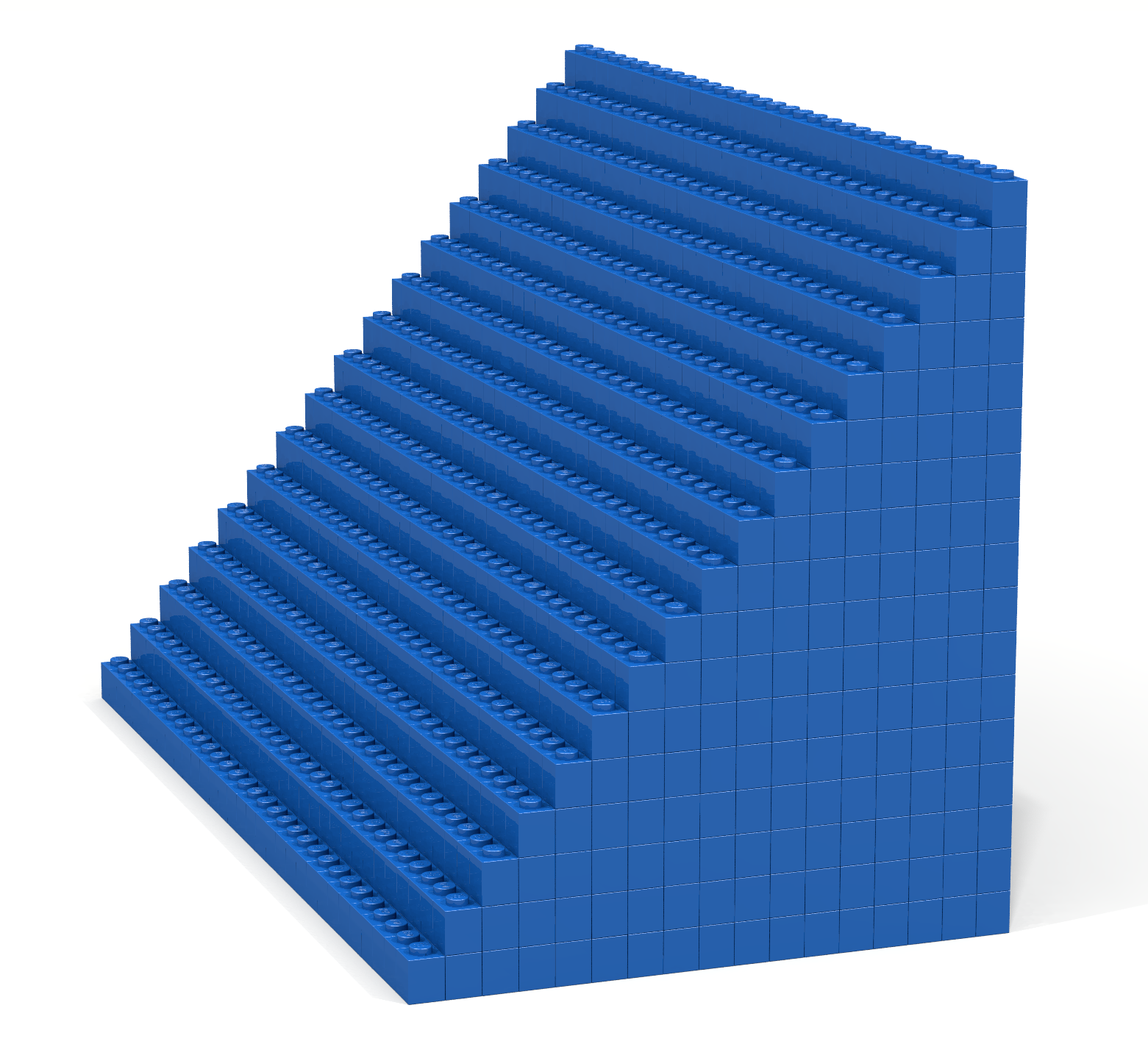
Write a Bricklayer program that uses traverseWithin and brick functions to create a wedge similar to the one shown in Figure 8.
Coding Exercise 9
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
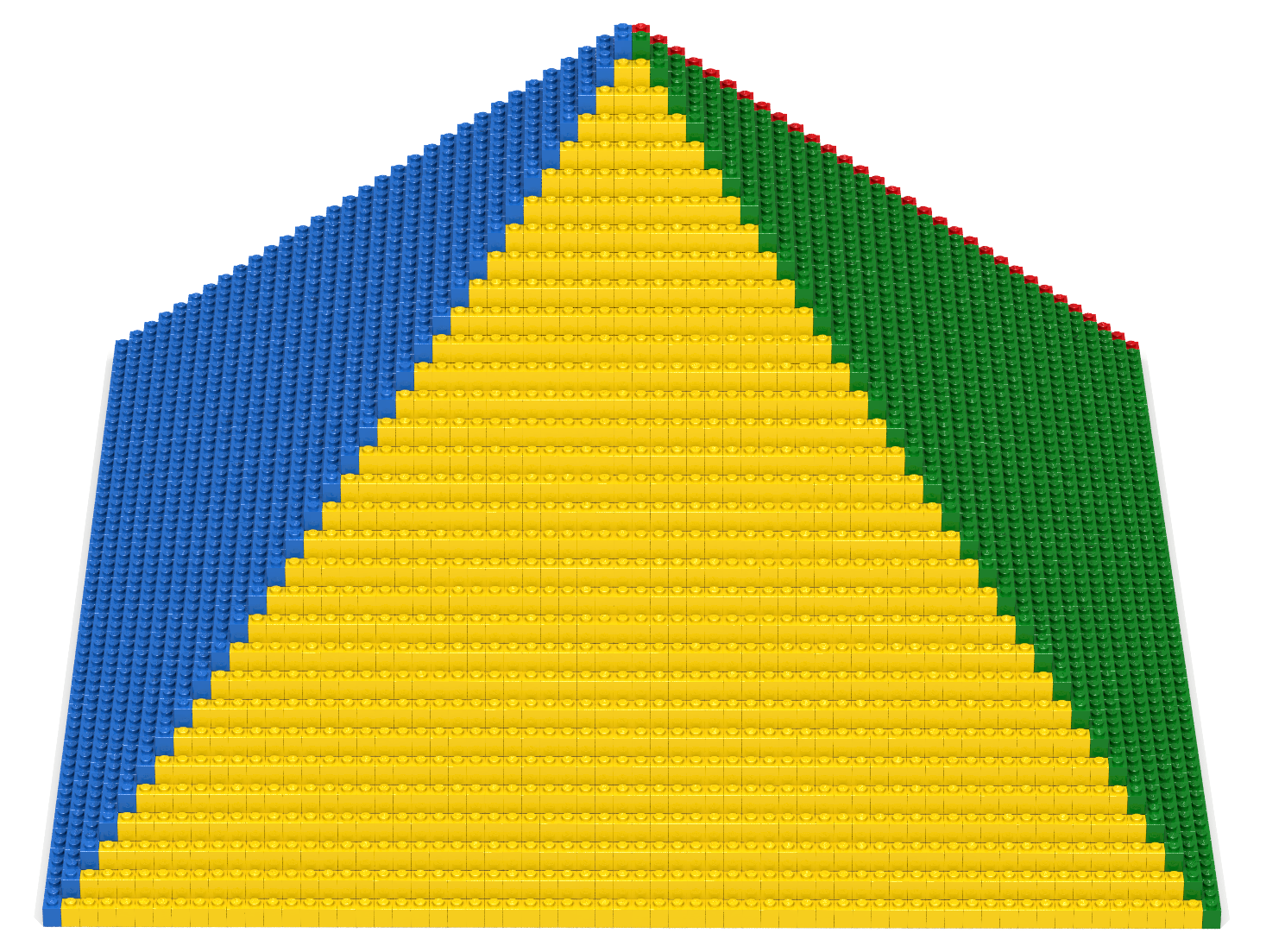
Write a Bricklayer program that uses traverseWithin and brick functions to create a tent-like wedge similar to the one shown in Figure 9.
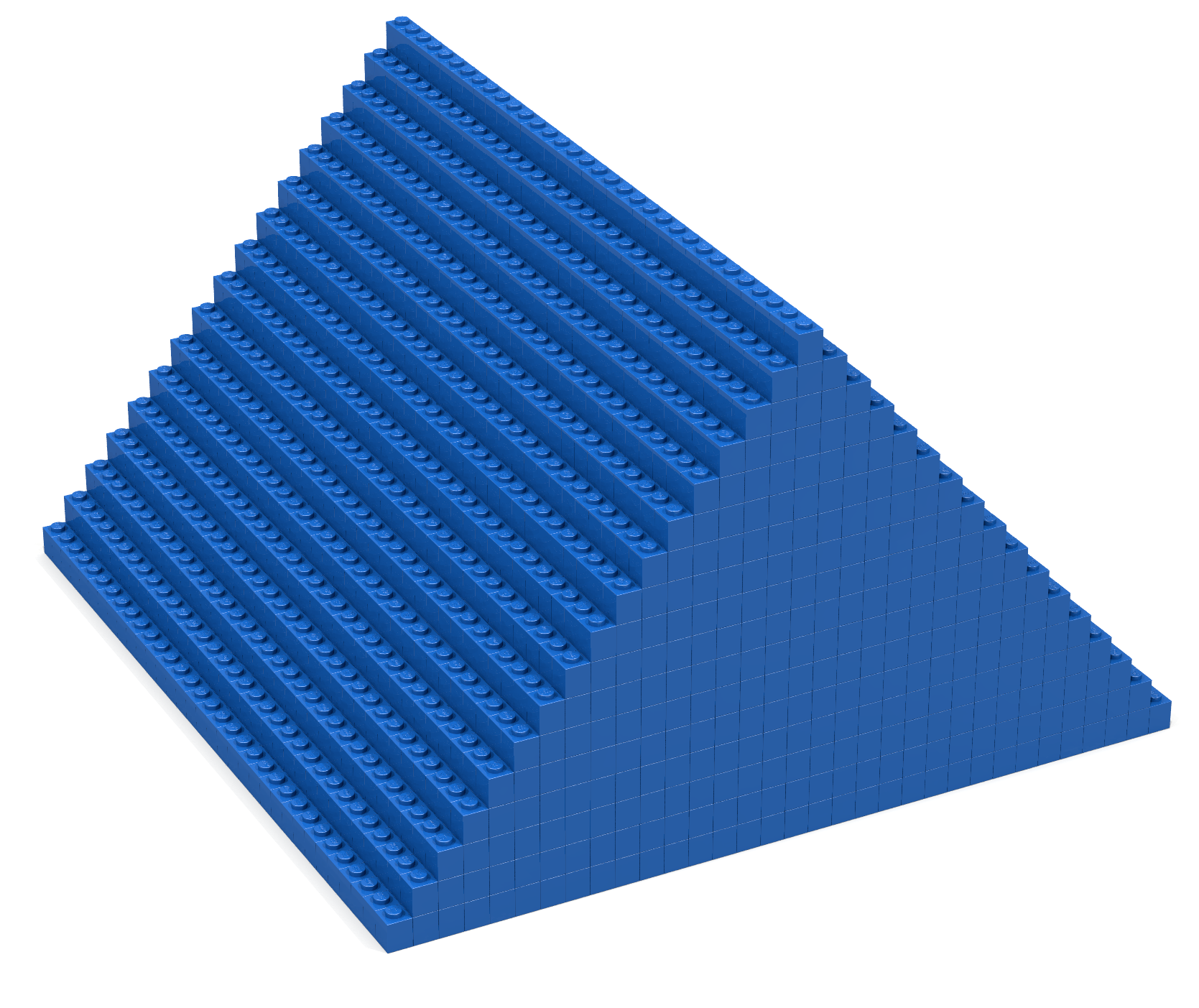
Coding Exercise 10
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
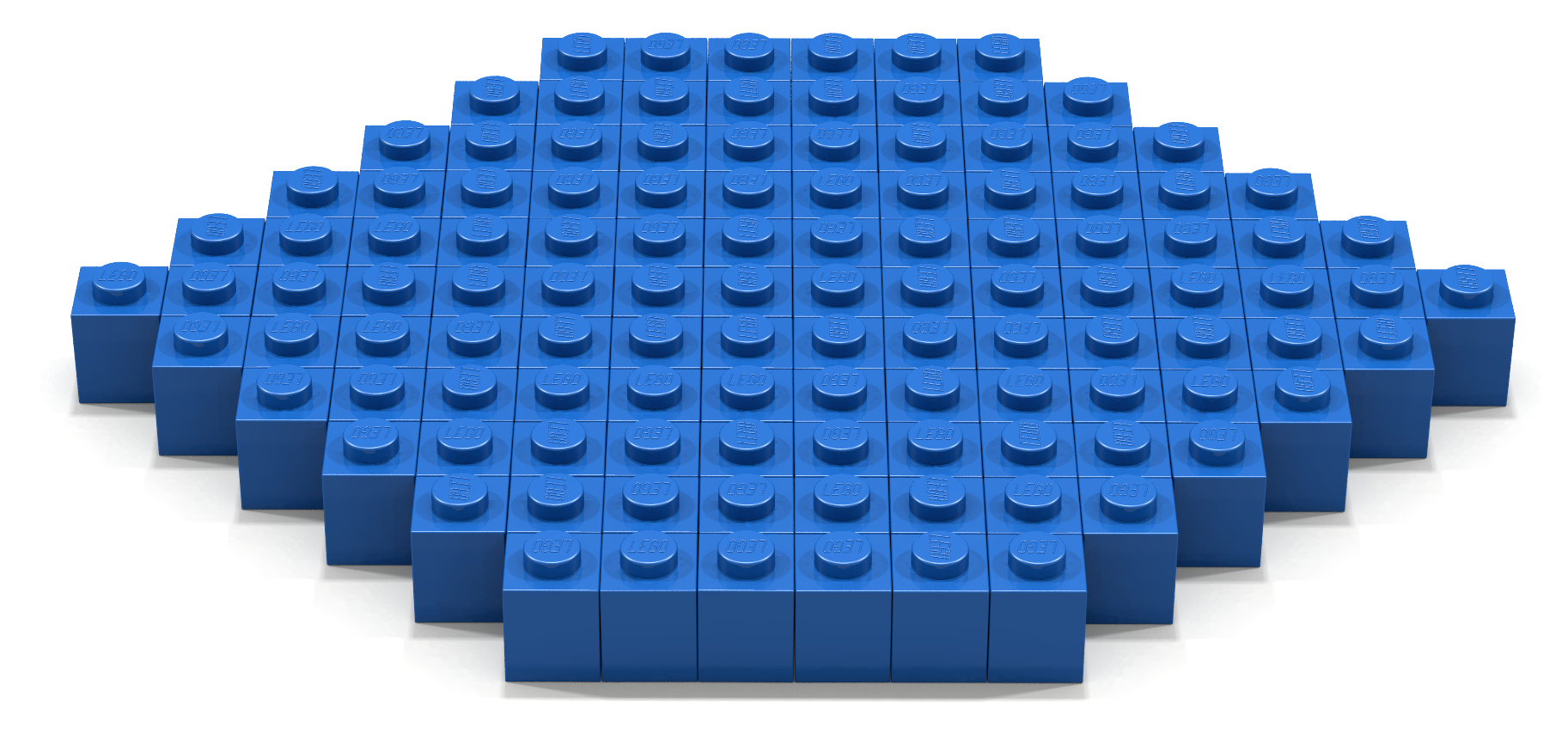
Write a Bricklayer program that uses traverseWithin and brick functions to create a pyramid similar to the one shown in Figure 10. Note that the top of this pyramid consists of four 1-bit bricks.
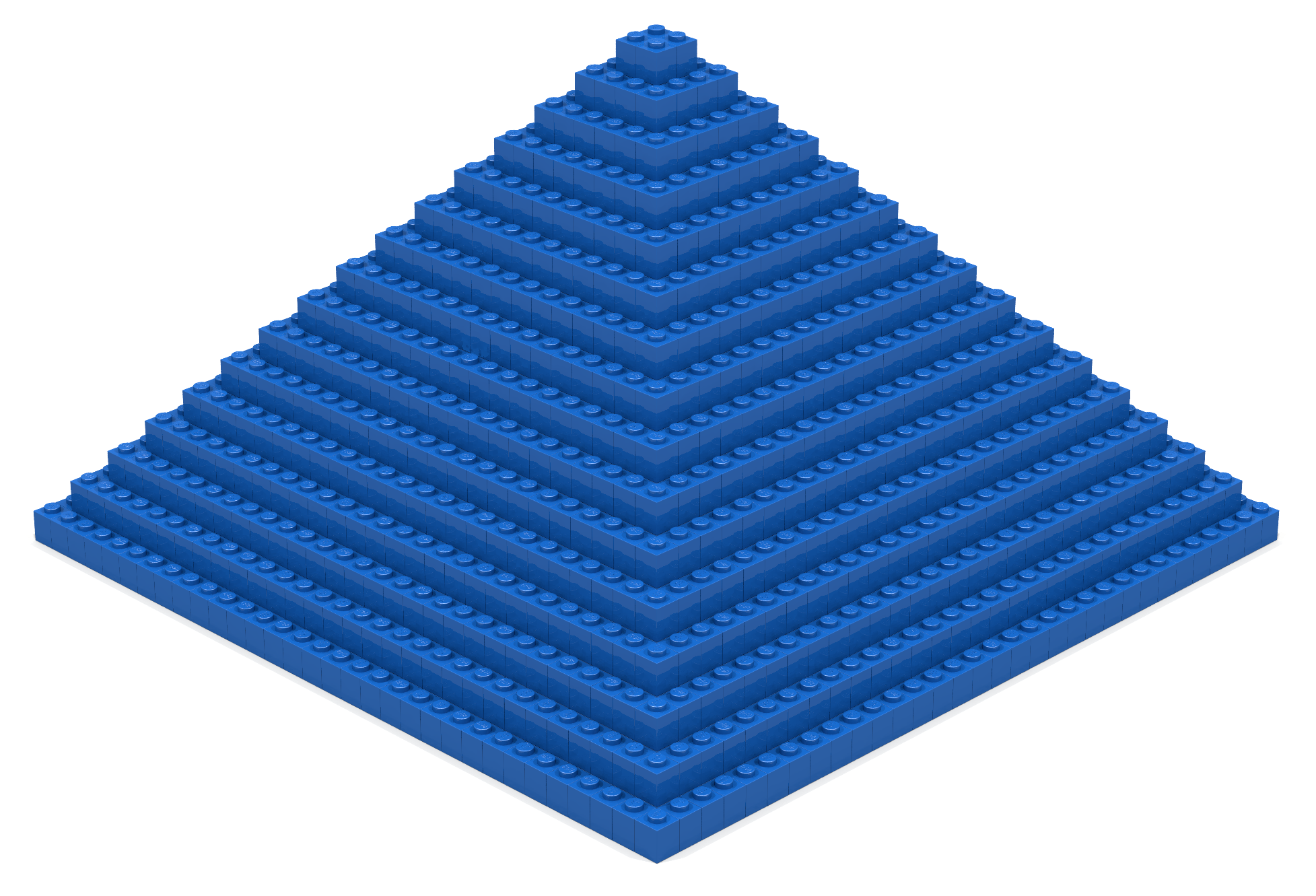
Coding Exercise 11
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
Write a Bricklayer program that uses traverseWithin and brick functions to create the artifact shown in Figure 11. Your solution should be general in the sense that it can be used (within minimal changes) to make an artifact of any size. More specifically, it should make use of the div operator.
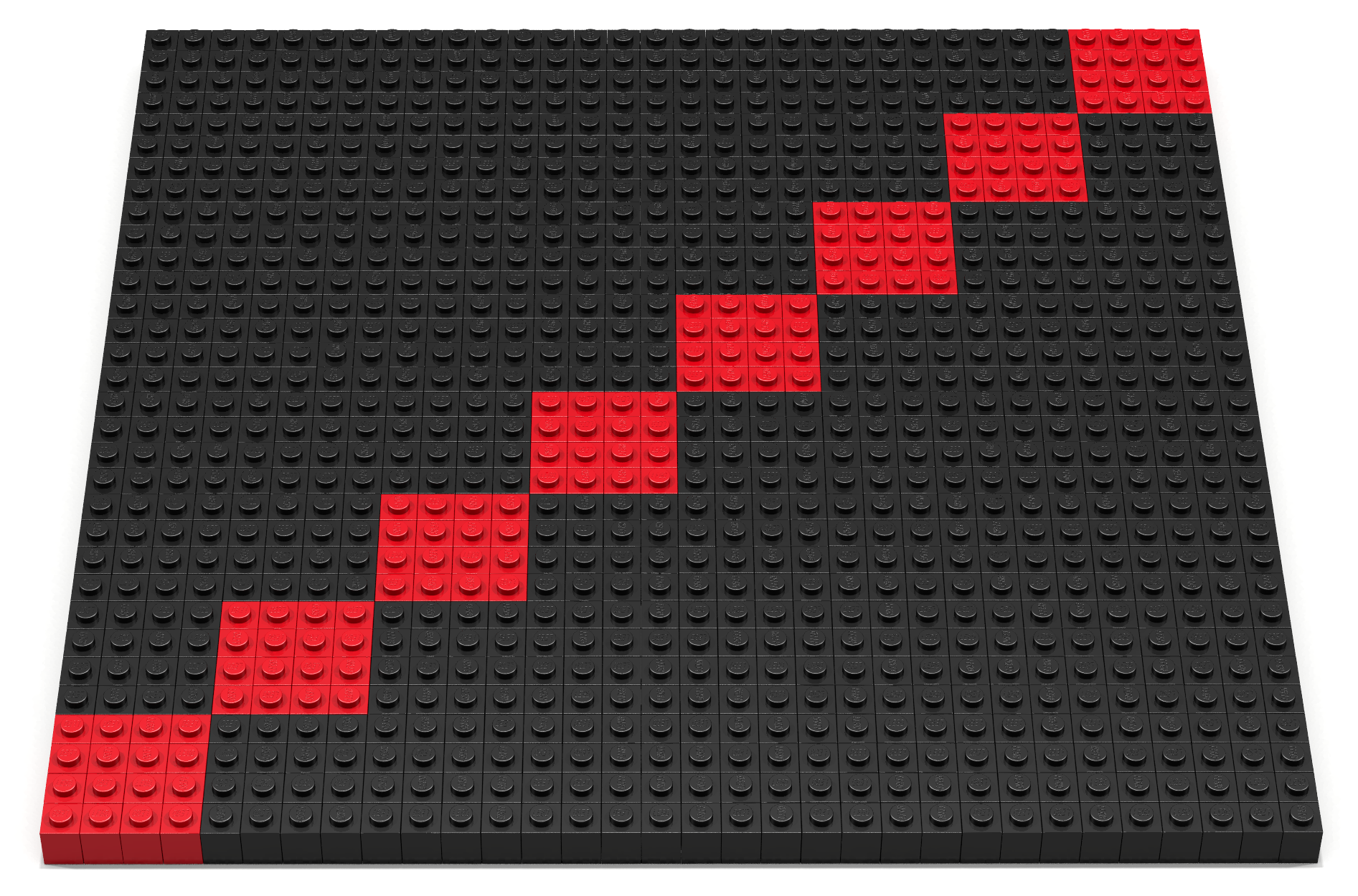
Coding Exercise 12
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
Write a Bricklayer program that uses traverseWithin and brick functions to create the artifact shown in Figure 12.
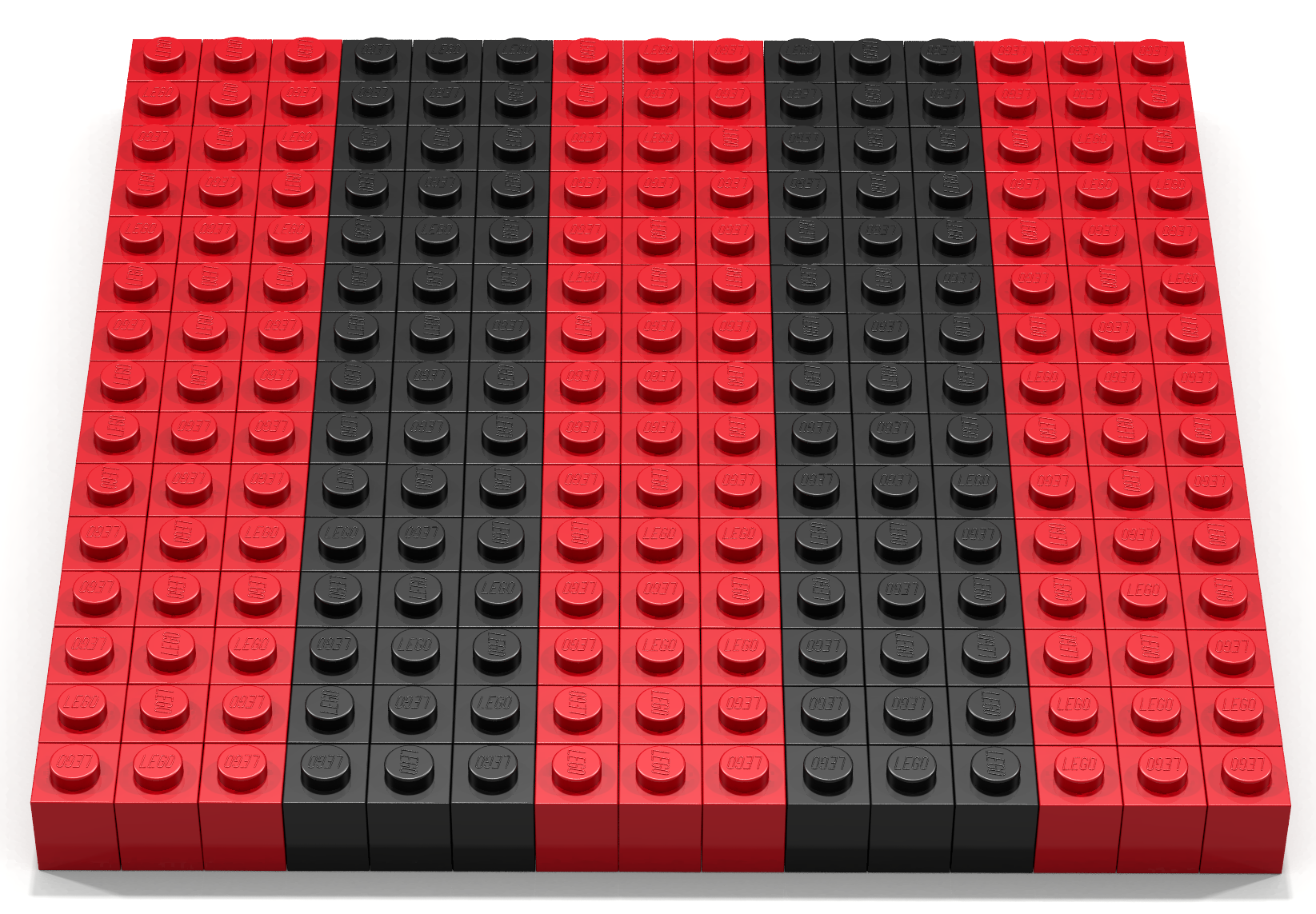
Coding Exercise 13
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
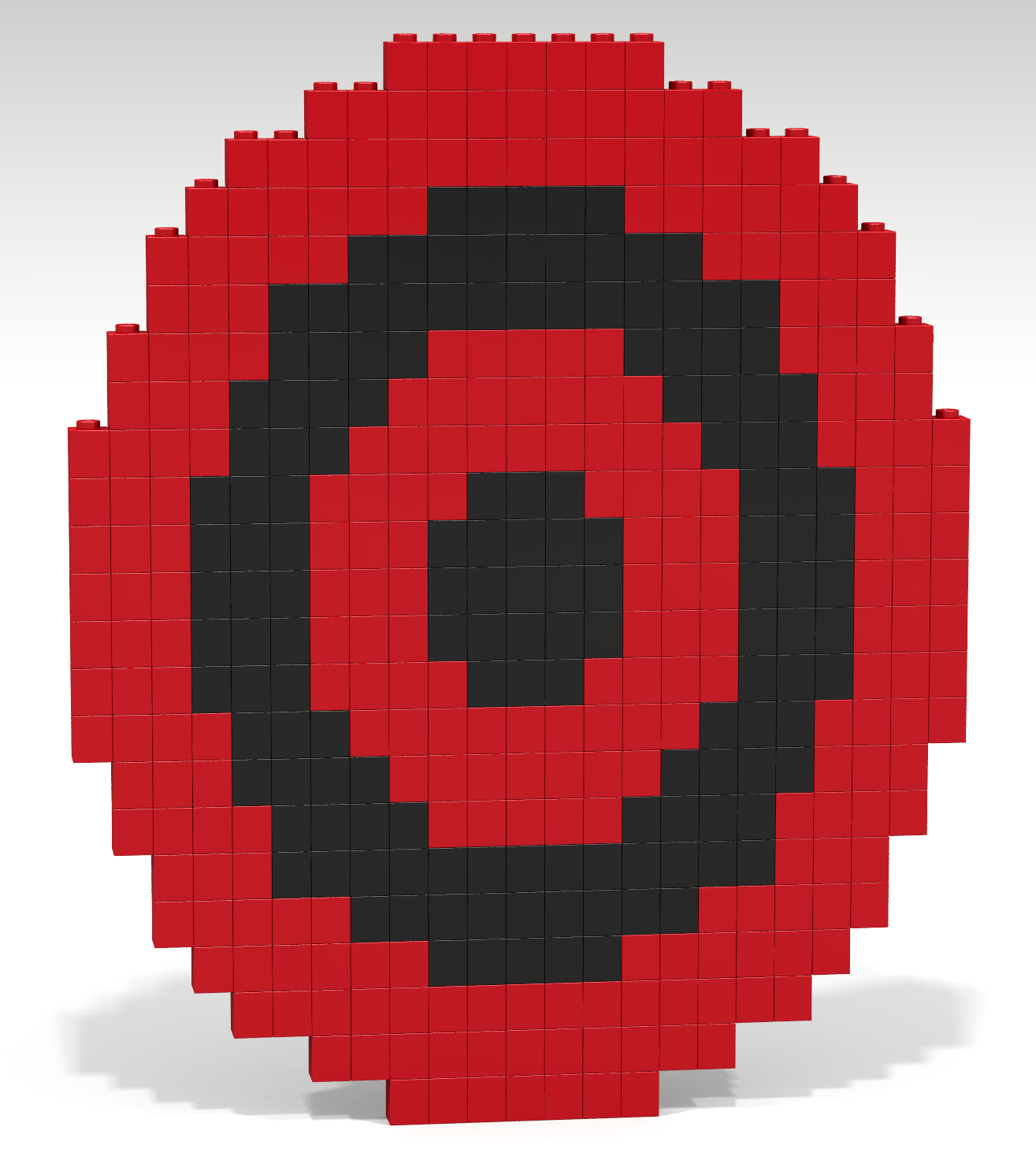
Write a Bricklayer program that uses traverseWithin and brick functions to create the target-like artifact shown in Figure 1. Your solution should have the property that additional rings will automatically be created as the radius of the target gets larger. Specifically, other than changing the radius no additional coding is necessary to create additional rings. Hint: adapt the conditional expression used to place red/black bricks along the x-axis to the radius of the circle you are creating. In other words, the properties asked of the x values are now asked of radius values.
Coding Exercise 14
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
LEGO bricks are taller than they are wide/deep. If you look down on the top of a brick the shape of a 1-bit brick will be a square (i.e., the x and z lengths of a brick are equal). In contrast, if you look at a brick from the side the shape of a 1-bit brick is rectangular. Specifically, the y length of the brick is larger than the x/z length. When building a circle in the xy-plane or yz-plane this difference needs to be compensated for, otherwise circles will appear (slightly) oval. Figure 14a shows a target in the xy-plane whose radius is 11 and whose bands have a width of 3. In Figure 14a no compensation is performed to take
into account the dierence in brick lengths along the x-dimension and y-dimension. Even though the target appears fairly round, measuring the width and height with a ruler confirms that the target is indeed taller than it is wide. In contrast, the target shown in Figure 14b has an appearance that is more circular. The target shown in Figure 14b has a radius of 15 and a band width of 4.
Write a Bricklayer program that uses traverseWithin and brick functions to create the target-like artifact shown in Figure 14b. Your solution should have the property that additional rings will automatically be created as the radius of the target gets larger. Specifically, other than changing the radius no additional coding is necessary to create additional rings. Please consult on-line documentation to find out the dimensions of LEGO bricks.


Coding Exercise 15
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
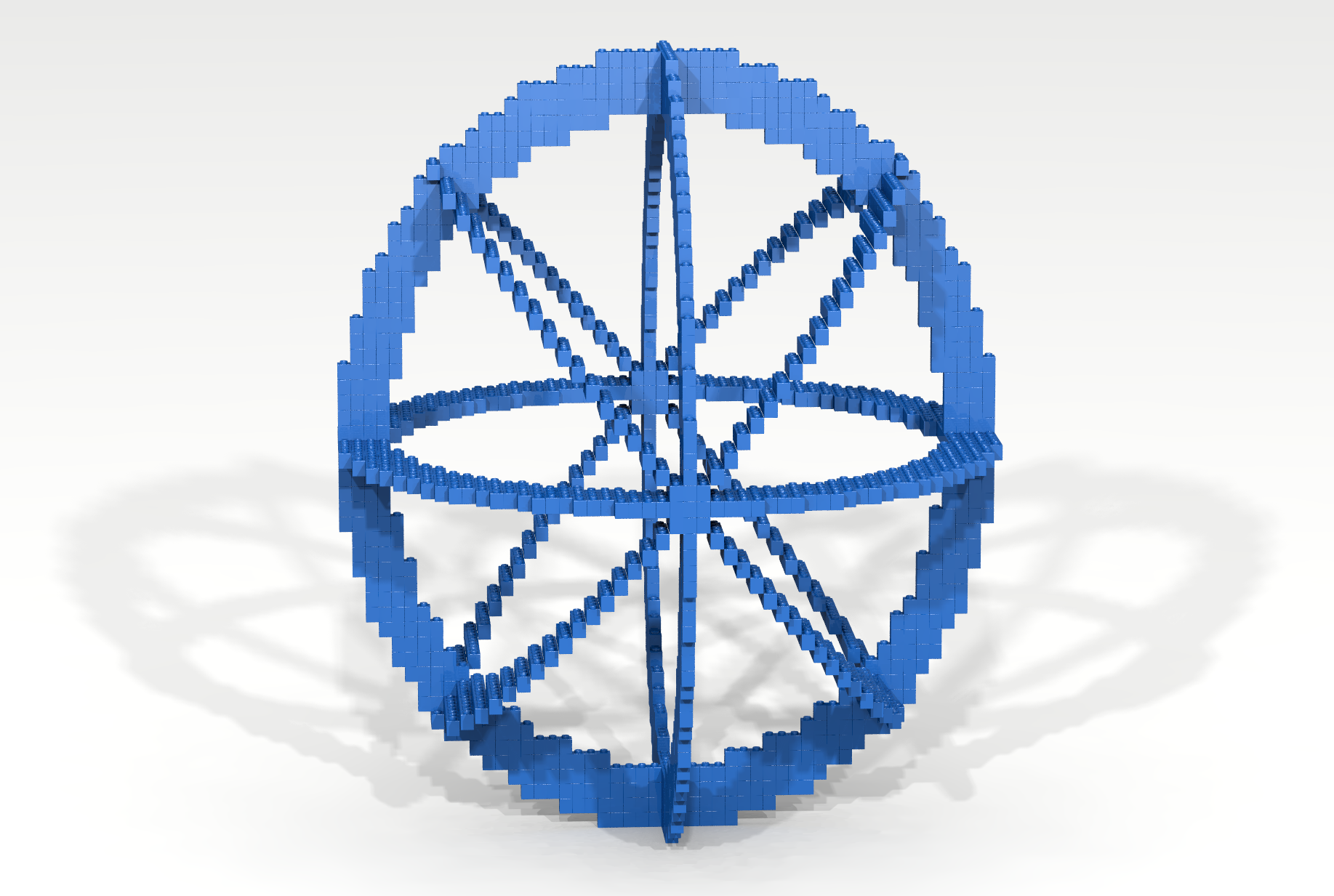
In the Basic Properties code-along an example was given showing how an artifact could be constructed by using a traversal and a brick function to slice a hollow sphere – keeping the desired parts and eliminating the rest. Adapt the techniques shown in the Basic Properties code-along to create the artifact shown in Figure 15.
Coding Exercise 16
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
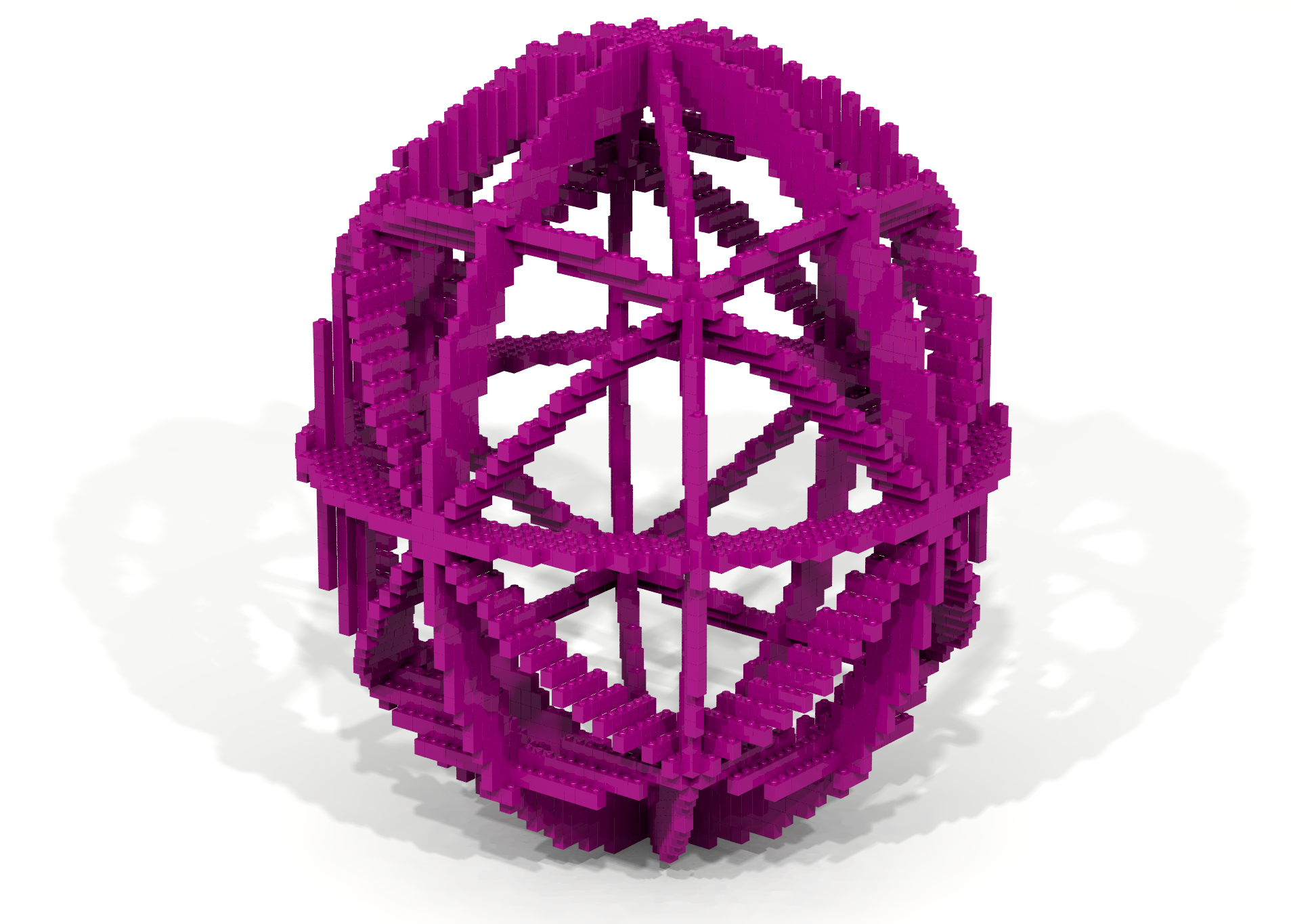
A celestial globe is projection of the sky onto the surface of a globe. At the center of a celestial globe resides the Earth. An armillary sphere is a celestial globe constructed from rings. As shown in Figures 16a and 16b, the number and kind of rings used to construct an armillary sphere can vary greatly from one sphere to another.
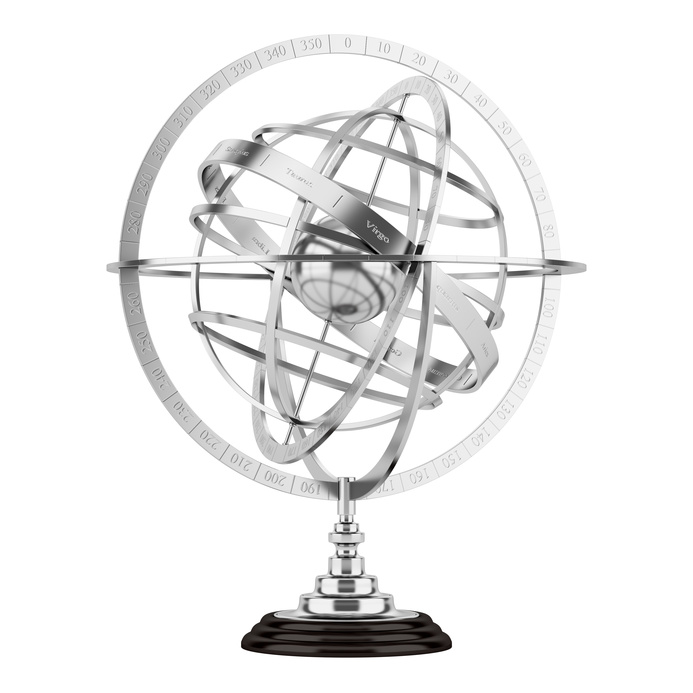
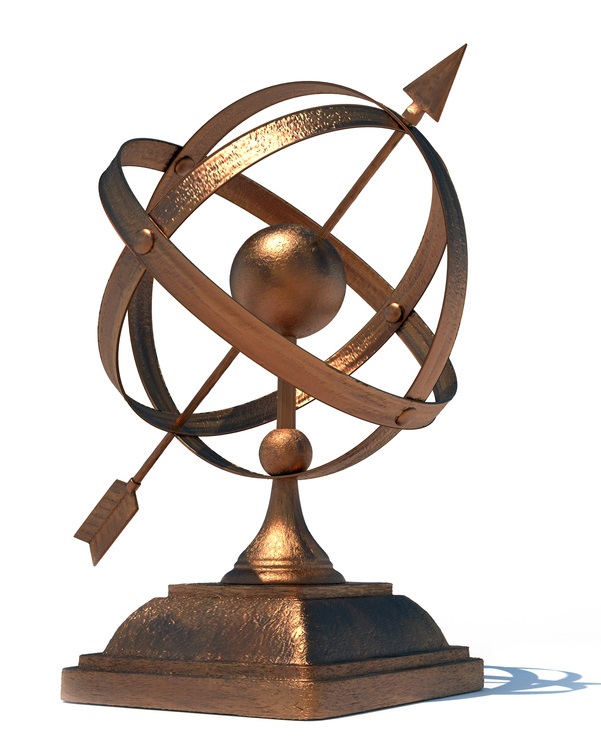


In the Basic Properties code-along an example was given showing how an artifact could be constructed by using a traversal and a brick function to slice a hollow sphere – keeping the desired parts and eliminating the rest. Adapt the techniques shown in the Basic Properties code-along to create the artifact shown in Figure 16c.
Coding Exercise 17
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
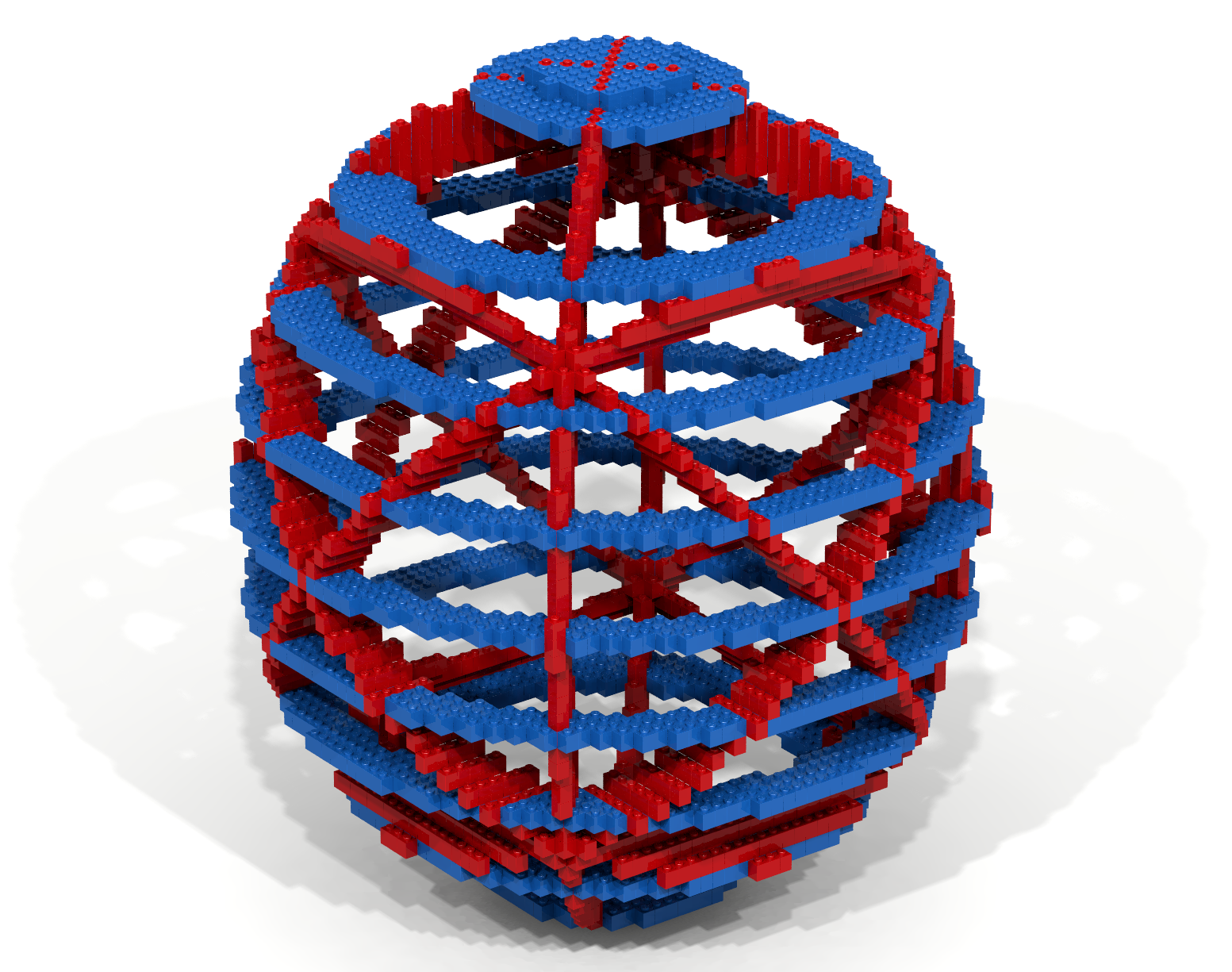
A celestial globe is projection of the sky onto the surface of a globe. At the center of a celestial globe resides the Earth. An armillary sphere is a celestial globe constructed from rings. See exercise 16 for examples of actual armillary spheres.
In the Basic Properties code-along an example was given showing how an artifact could be constructed by using a traversal and a brick function to slice a hollow sphere – keeping the desired parts and eliminating the rest. Adapt the techniques shown in the Basic Properties code-along to create the artifact shown in Figure 17.
Coding Exercise 18
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
A celestial globe is projection of the sky onto the surface of a globe. At the center of a celestial globe resides the Earth. An armillary sphere is a celestial globe constructed from rings. See exercise 16 for examples of actual armillary spheres.
In the Basic Properties code-along an example was given showing how an artifact could be constructed by using a traversal and a brick function to slice a hollow sphere – keeping the desired parts and eliminating the rest. Adapt the techniques shown in the Basic Properties code-along to create the artifact shown in Figure 18.
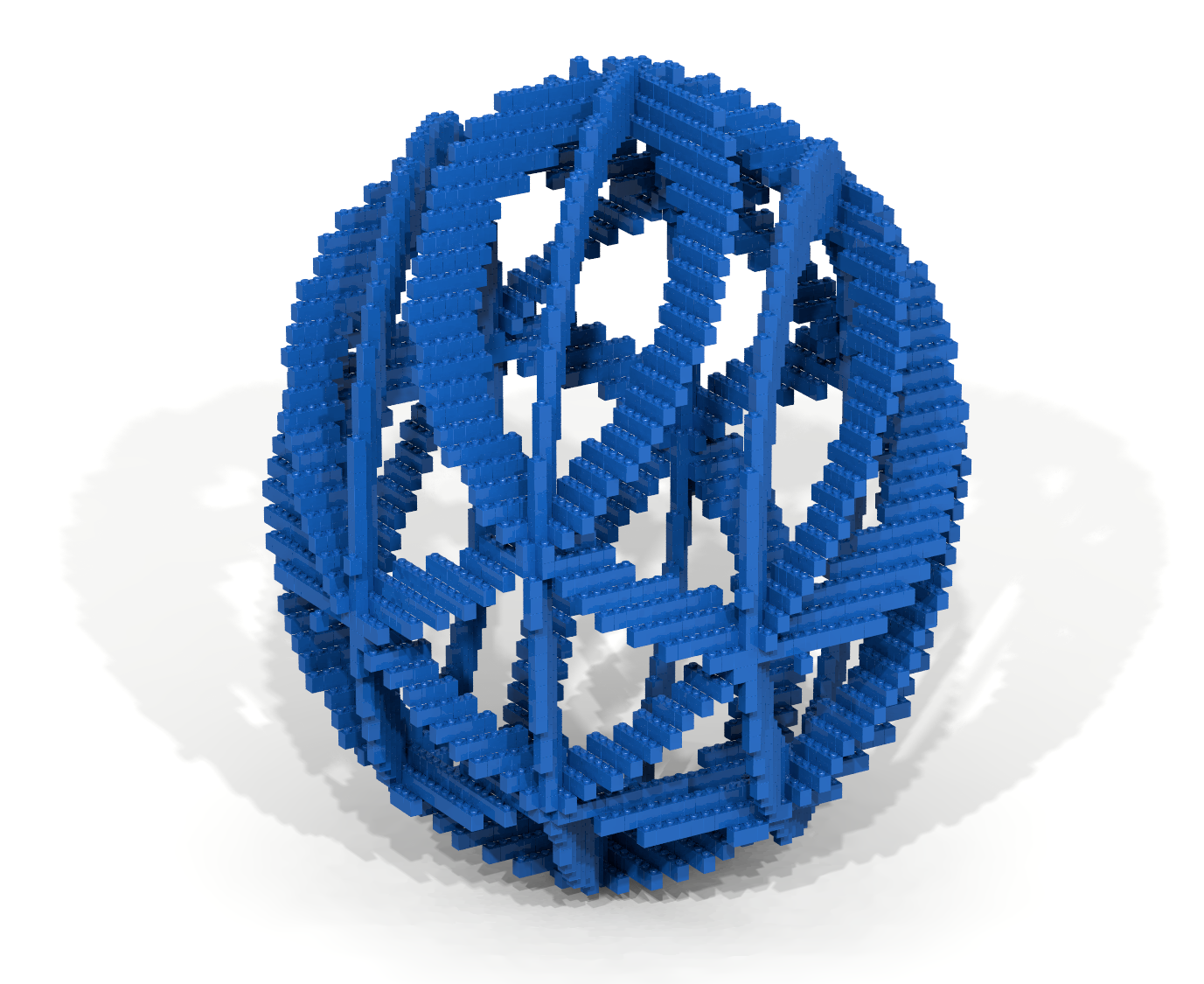
Coding Exercise 19
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
When combined with traverseWithin, the mod operator can be used to create repeating patterns. The artifact shown in Figure 19 is a composition of three distinct repeating artifacts. The GREEN artifact is a vertical xy-plane that is positioned diagonally across the z-axis. The mod operator is used to create three repetitions of the GREEN artifact. The BLUE and YELLOW artifacts are slanted xy-planes in which the mod operator is also used to create three repetitions of each artifact.
Write a Bricklayer program that creates an artifact similar to the one shown in Figure 19. Hint, first focus on creating a single GREEN plane. Then focus on creating a single BLUE/YELLOW plane. After this has been accomplished introduce the mod operator to create repeating planes. An example of how the mod operator can be used to create a repeating pattern can be found here. Note that the mod operator also can be applied to x, y or z individually.
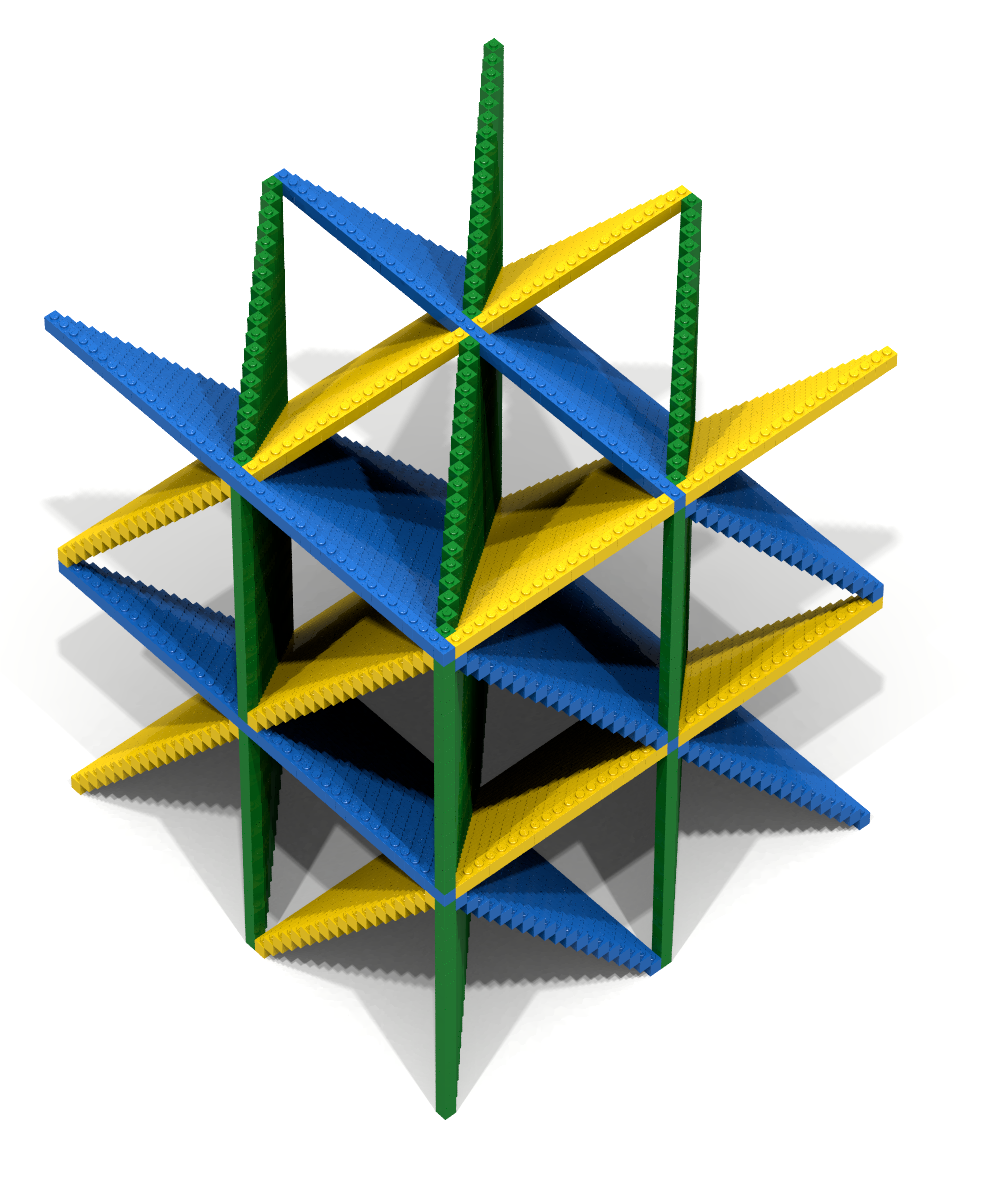
Coding Exercise 20
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
In the Slanted Triangles code-along, ideas were discussed and examples given on how to create slanted triangles having various orientations. Adapt the ideas discussed in that code-along to create the artifact shown in Figure 20.
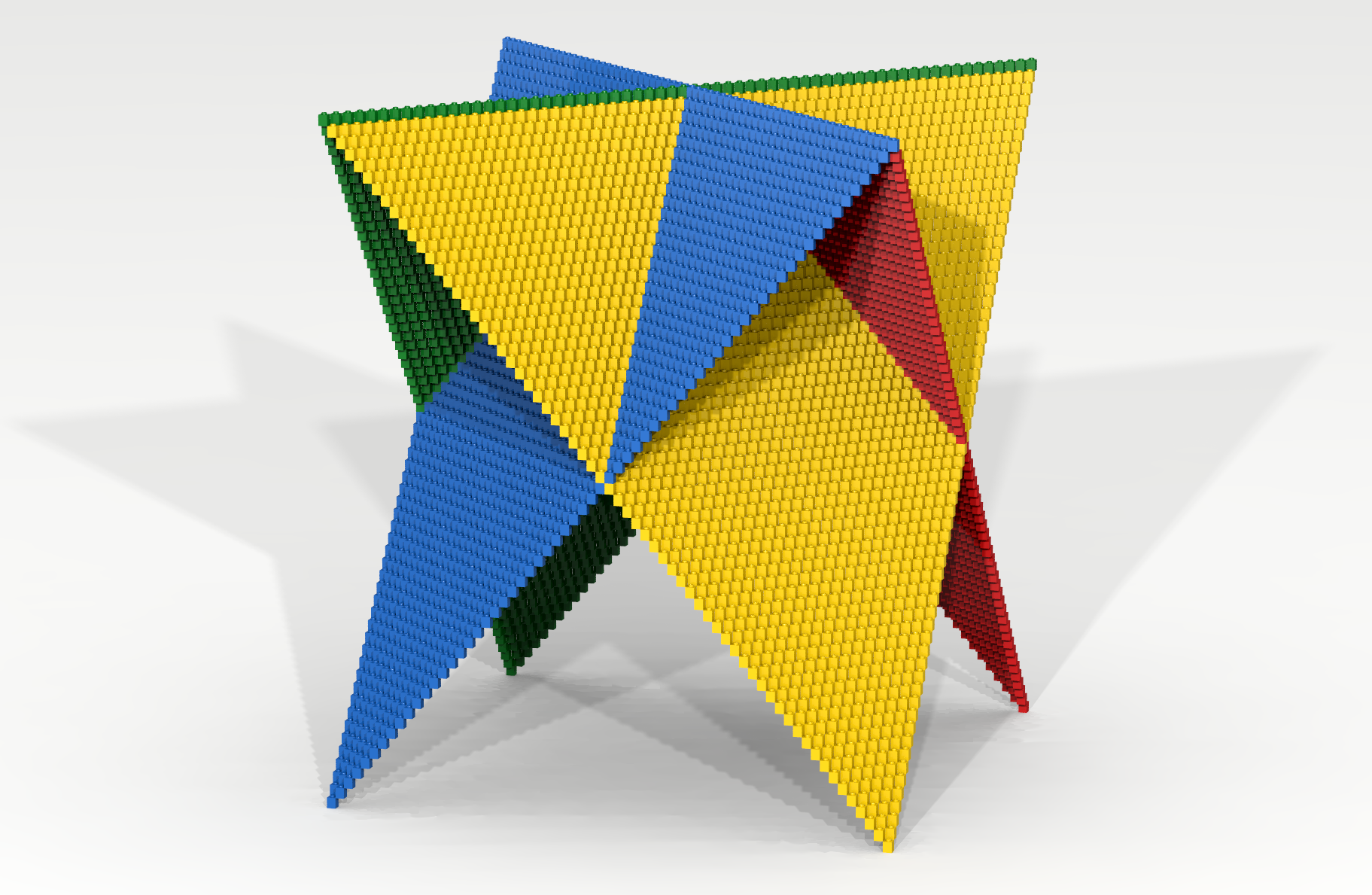
Coding Exercise 21
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
In the Slanted Triangles code-along, ideas were discussed and examples given on how to create slanted triangles having various orientations. Adapt the ideas discussed in that code-along to create the artifact shown in Figures 21a and 21b.
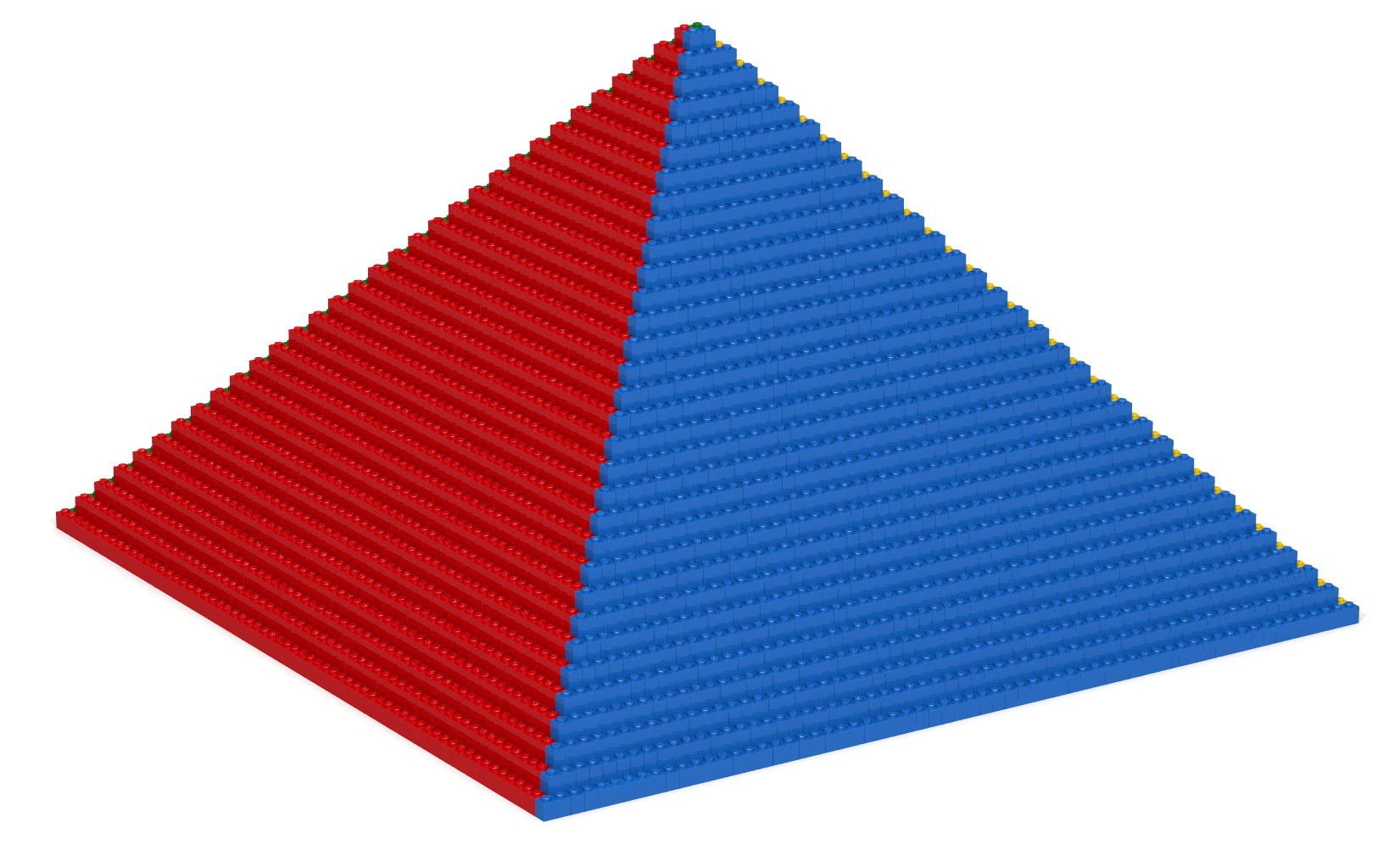
Coding Exercise 22
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
The ninth episode of the third (and sadly final) season of the original Star Trek series was titled “The Tholian Web“. In this episode two Tholian ships attempt to capture the Enterprise in an energy web consisting of criss-crossed lines. The Enterprise must figure out a way to save Captain Kirk and escape before the Tholian ships complete their energy web.

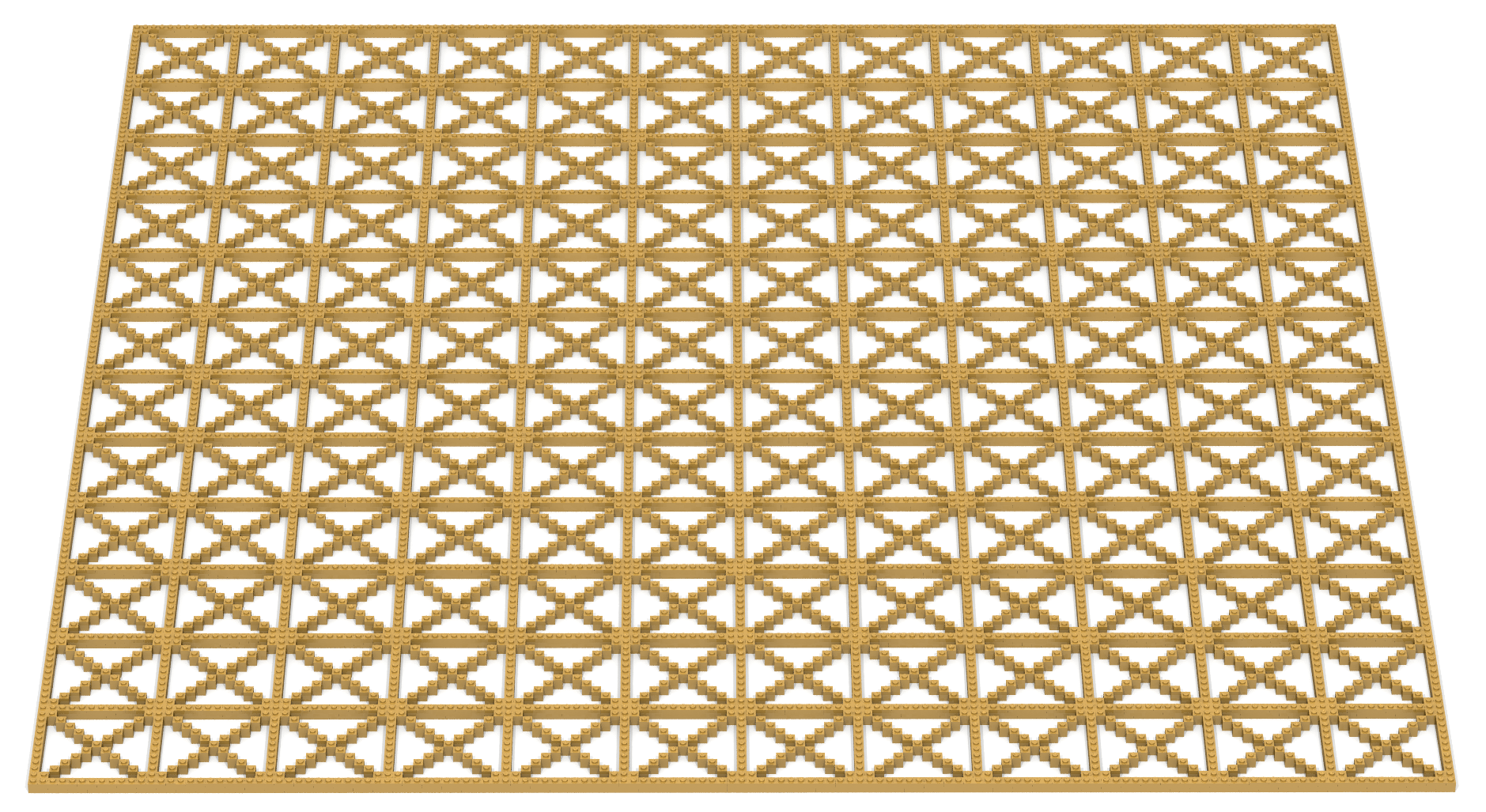
Write a Bricklayer program that creates a 2D Tholian Web-like artifact similar to the one shown in Figure 22b. Recall that when combined with traverseWithin, the mod operator can be used to create repeating patterns.
Coding Exercise 23
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
Write a Bricklayer program that creates a four-color sphere similar to the one shown in Figure 23. Your program should NOT make use of the setMySpace function. Instead, the traverseWithin function should be used. The basic idea is to create a hollow sphere consisting of a single color and to then use one or more traversals to replace portions of the sphere with different colored bricks. Note how all four colors come together at the front of the sphere.
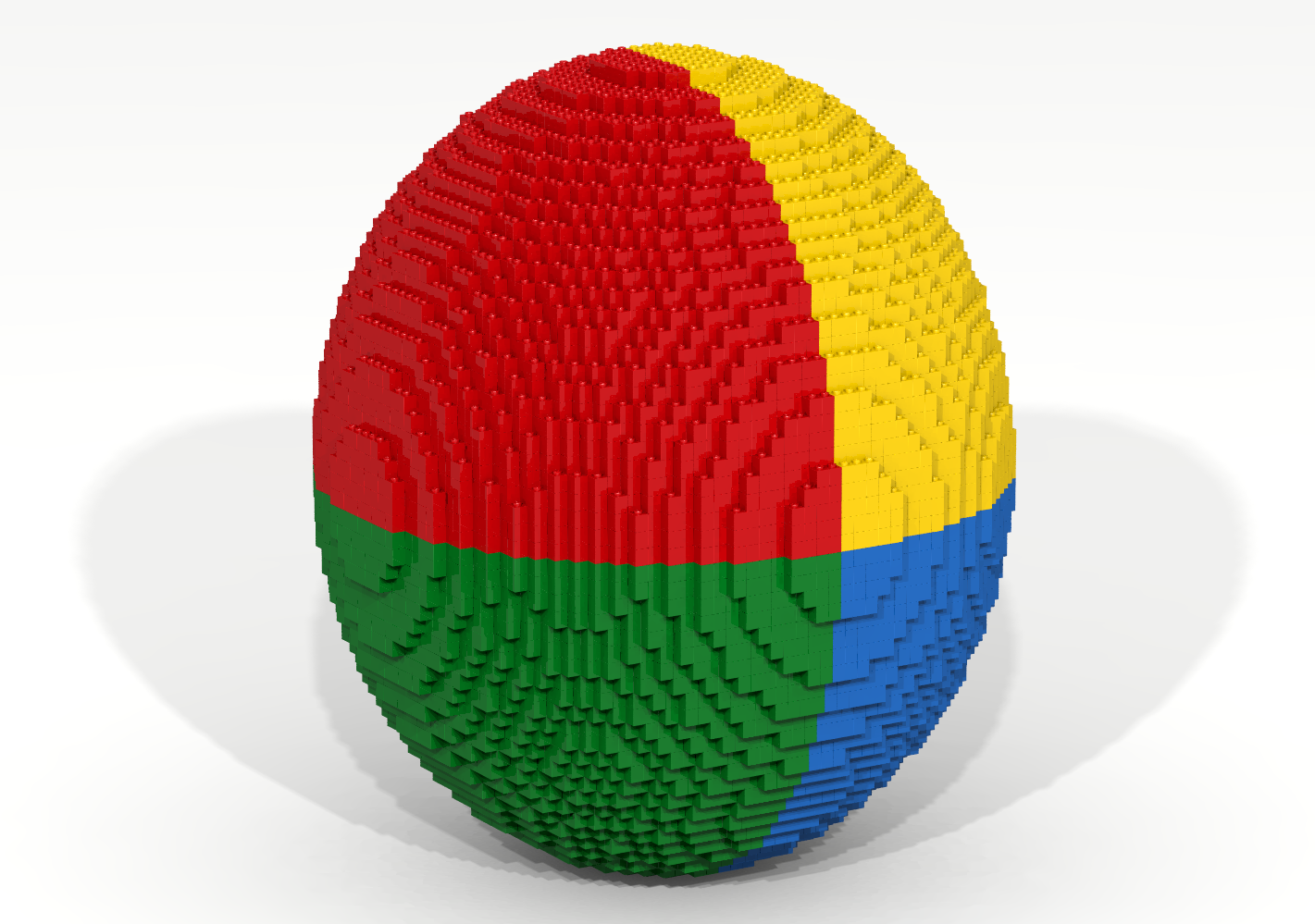

Coding Exercise 24
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
When combined with traversals, the mod operator can be used to create repeating patterns. In this context, the div operator can be used to control the size of the pattern that is to be repeated.
Write a Bricklayer program that creates a chess cube shown in Figure 24. One way to approach this problem is to first figure out how to use mod to create a chess cube whose individual BLACK/WHITE cubes are 1x1x1 bricks. Then experiment with how the div operator can be used to increase the size of the individual BLACK/WHITE cubes.
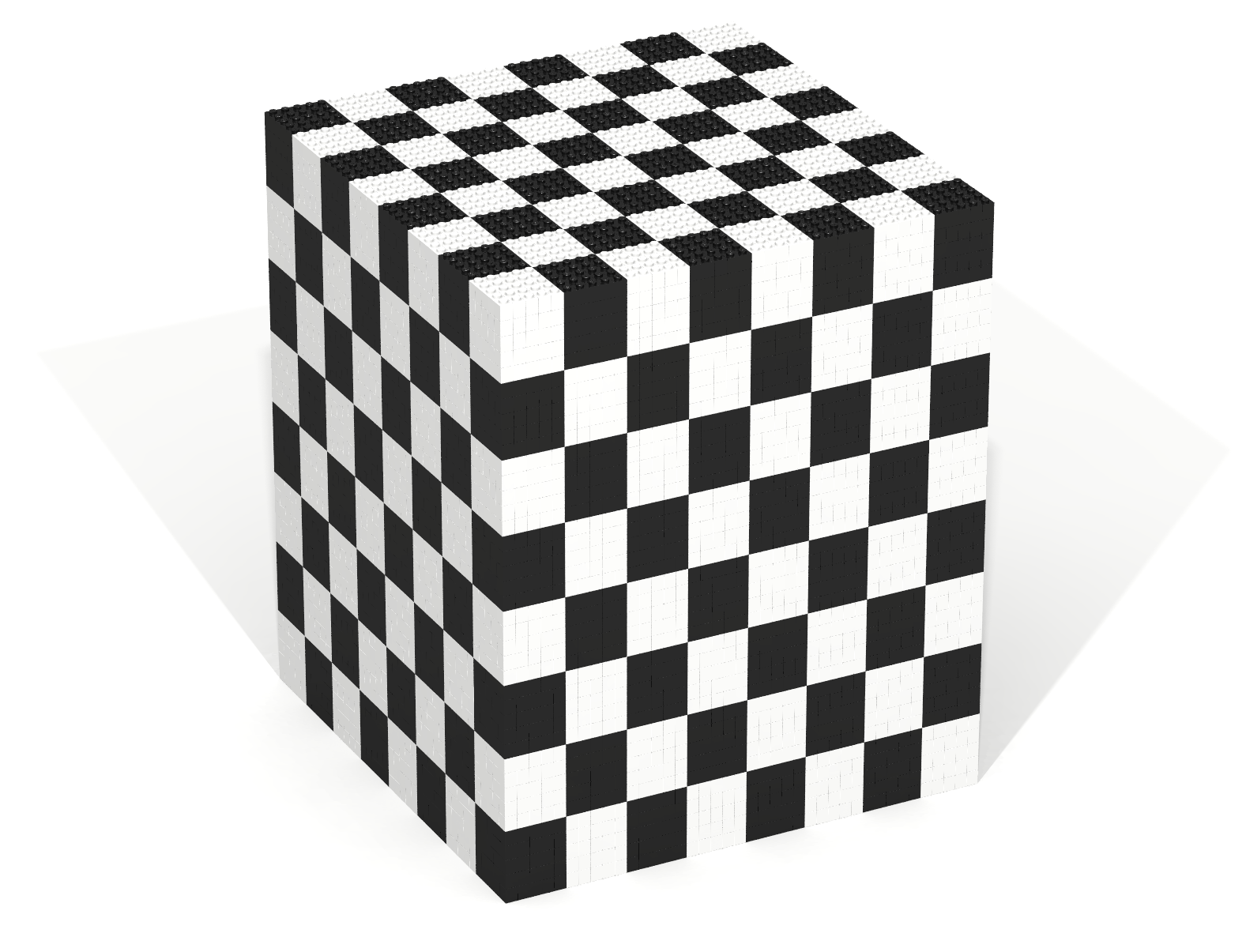

Coding Exercise 25
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
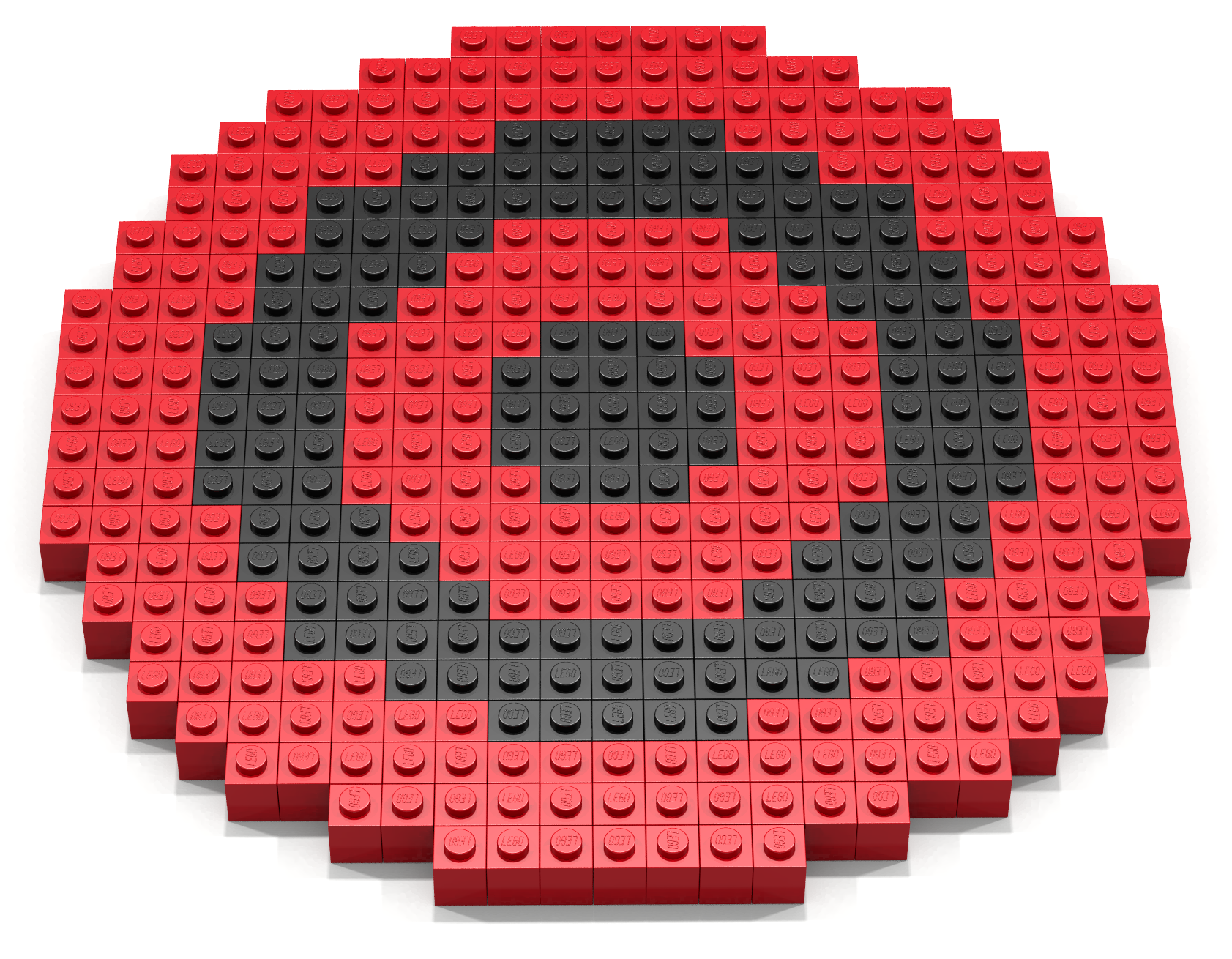
Pokémon Go is a game for iPhone and Android devices that combines the virtual world in which Pokémon live with the real world in which the players live. The main activities of the game include the following: (1) hunting and catching Pokémon, (2) visiting PokéStops to gather supplies, (3) battling and joining PokéGyms, and (4) hatching eggs. The game overlays the virtual world of the Pokémon on the real world. Positional data is used to track a player’s position and relate this position to objects in the Pokémon world.
The primary activity in the game is to catch Pokémon, which can be caught using a variety of balls. The most common ball is the Poké Ball. Write a Bricklayer program that creates a Poké Ball similar to the one shown in Figure 25. This Poké Ball was was created using hollowSphere, ringY, ringZ, and traverseWithin functions.
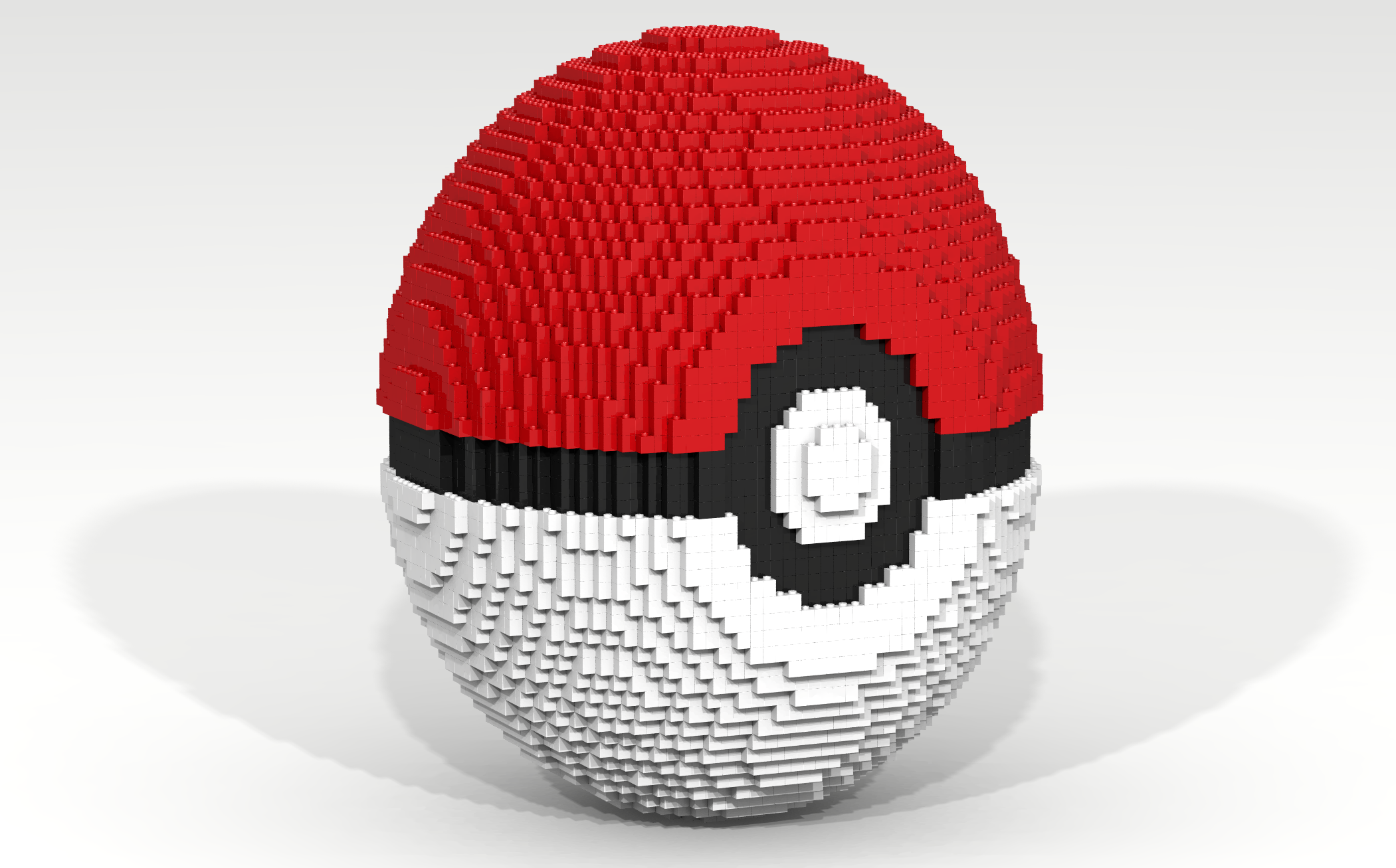

Coding Exercise 26
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
Pokémon Go is a game for iPhone and Android devices that combines the virtual world in which Pokémon live with the real world in which the players live. The main activities of the game include the following: (1) hunting and catching Pokémon, (2) visiting PokéStops to gather supplies, (3) battling and joining PokéGyms, and (4) hatching eggs. The game overlays the virtual world of the Pokémon on the real world. Positional data is used to track a player’s position and relate this position to objects in the Pokémon world.
The primary activity in the game is to catch Pokémon, which can be caught using a variety of balls. One such ball is the Great Ball which becomes available when a player reaches level 12. Write a Bricklayer program that creates a Great Ball similar to the one shown in Figure 26. This Great Ball was was created using hollowSphere, ringY, ringZ, and traverseWithin functions.
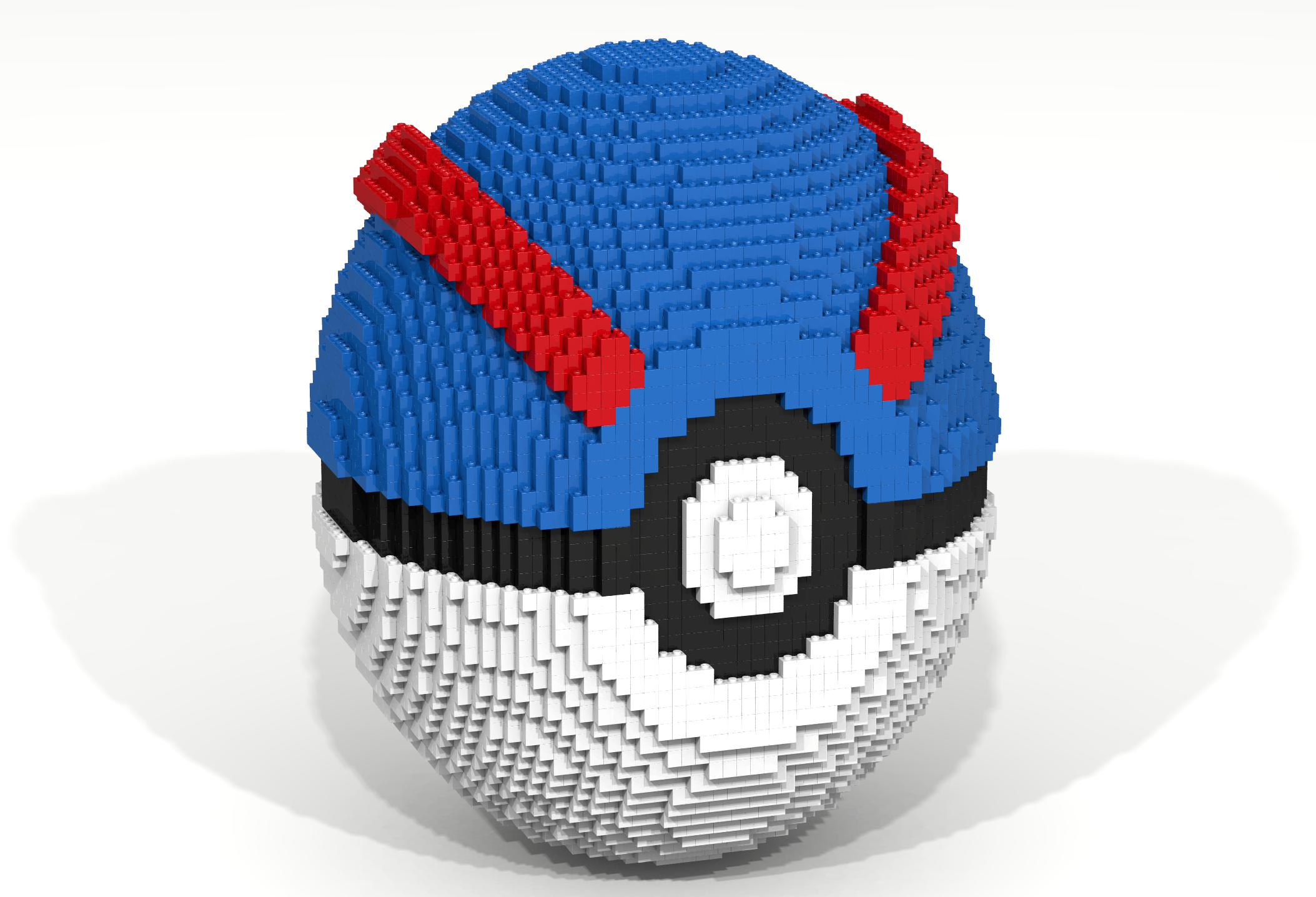

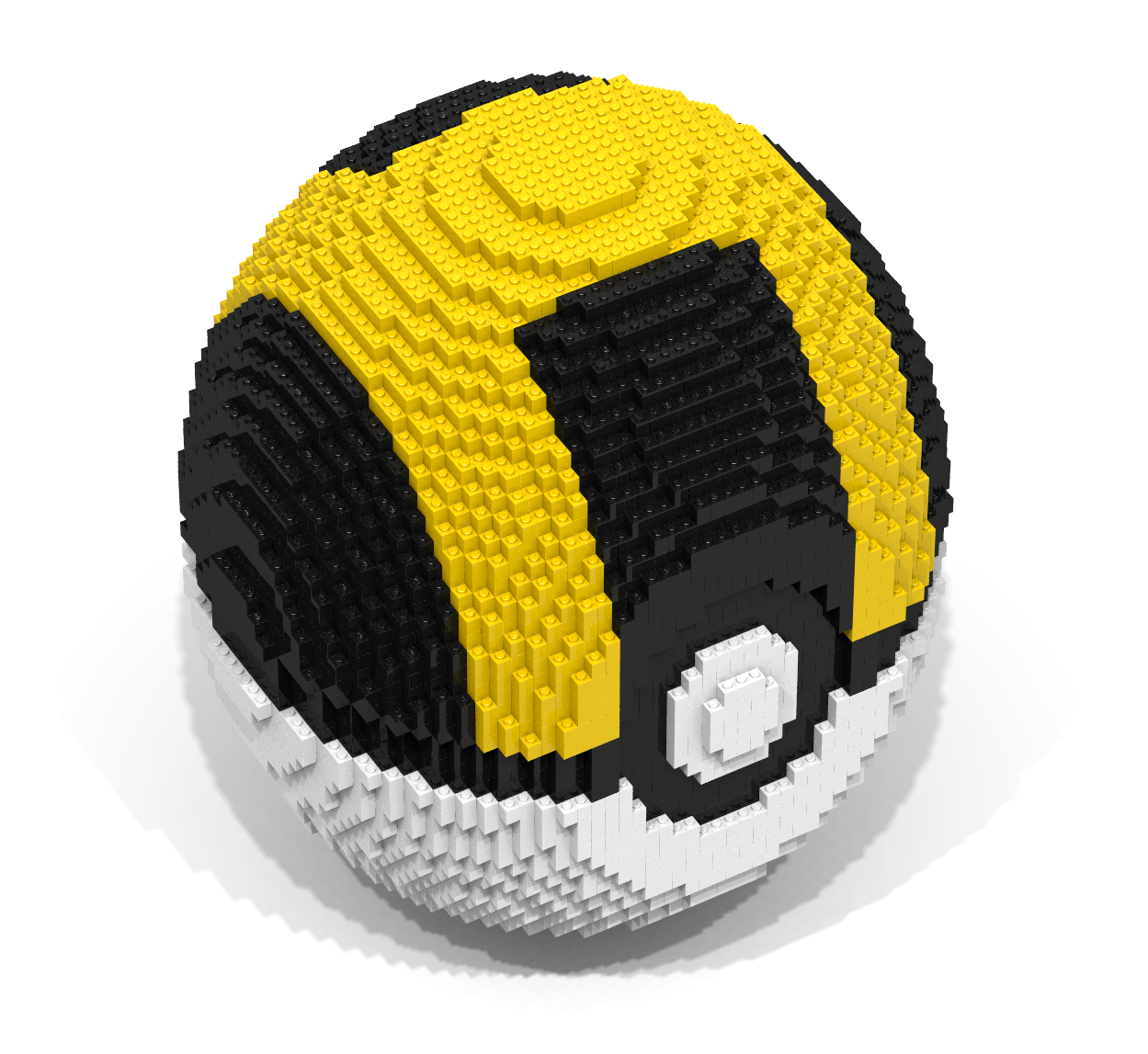
Coding Exercise 27
| Prerequisite Concepts | 7, 12 |
| Key Concepts | 20, 21, 22, 23 |
Pokémon Go is a game for iPhone and Android devices that combines the virtual world in which Pokémon live with the real world in which the players live. The main activities of the game include the following: (1) hunting and catching Pokémon, (2) visiting PokéStops to gather supplies, (3) battling and joining PokéGyms, and (4) hatching eggs. The game overlays the virtual world of the Pokémon on the real world. Positional data is used to track a player’s position and relate this position to objects in the Pokémon world.
The primary activity in the game is to catch Pokémon, which can be caught using a variety of balls. One such ball is the Ultra Ball which becomes available when a player reaches level 20. Write a Bricklayer program that creates an Ultra Ball similar to the one shown in Figure 27. This Ultra Ball was was created using hollowSphere, ringY, ringZ, and traverseWithin functions.
